Stable C0T-1 repeat RNA is abundant and is associated with euchromatic interphase chromosomes
- PMID: 24581492
- PMCID: PMC4023122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.042
Stable C0T-1 repeat RNA is abundant and is associated with euchromatic interphase chromosomes
Abstract
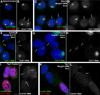
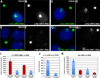
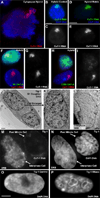
Recent studies recognize a vast diversity of noncoding RNAs with largely unknown functions, but few have examined interspersed repeat sequences, which constitute almost half our genome. RNA hybridization in situ using C0T-1 (highly repeated) DNA probes detects surprisingly abundant euchromatin-associated RNA comprised predominantly of repeat sequences (C0T-1 RNA), including LINE-1. C0T-1-hybridizing RNA strictly localizes to the interphase chromosome territory in cis and remains stably associated with the chromosome territory following prolonged transcriptional inhibition. The C0T-1 RNA territory resists mechanical disruption and fractionates with the nonchromatin scaffold but can be experimentally released. Loss of repeat-rich, stable nuclear RNAs from euchromatin corresponds to aberrant chromatin distribution and condensation. C0T-1 RNA has several properties similar to XIST chromosomal RNA but is excluded from chromatin condensed by XIST. These findings impact two "black boxes" of genome science: the poorly understood diversity of noncoding RNA and the unexplained abundance of repetitive elements.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
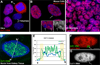
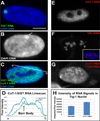
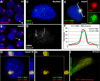
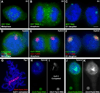
Comment in
-
Interphase chromatin LINEd with RNA.Cell. 2014 Feb 27;156(5):864-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.005. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24581484
References
-
- Britten RJ, Kohne DE. Repeated sequences in DNA: Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968;161:529–540. - PubMed
-
- Bynum JW, Volkin E. Chromatin-associated RNA: differential extraction and characterization. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1980;607:304–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

