Staphylococcus aureus toxins
- PMID: 24581690
- PMCID: PMC3942668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.11.004
Staphylococcus aureus toxins
Abstract
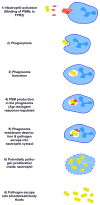
Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous pathogen that causes a variety of severe diseases. The virulence of S. aureus is defined by a large repertoire of virulence factors, among which secreted toxins play a preeminent role. Many S. aureus toxins damage biological membranes, leading to cell death. In particular, S. aureus produces potent hemolysins and leukotoxins. Among the latter, some were recently identified to lyse neutrophils after ingestion, representing an especially powerful weapon against bacterial elimination by innate host defense. Furthermore, S. aureus secretes many factors that inhibit the complement cascade or prevent recognition by host defenses. Several further toxins add to this multi-faceted program of S. aureus to evade elimination in the host. This review will give an overview over S. aureus toxins focusing on recent advances in our understanding of how leukotoxins work in receptor-mediated or receptor-independent fashions.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Francis JS, Doherty MC, Lopatin U, Johnston CP, Sinha G, Ross T, Cai M, Hansel NN, Perl T, Ticehurst JR, et al. Severe community-onset pneumonia in healthy adults caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:100–107. - PubMed
-
- Miller LG, Perdreau-Remington F, Rieg G, Mehdi S, Perlroth J, Bayer AS, Tang AW, Phung TO, Spellberg B. Necrotizing fasciitis caused by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Los Angeles. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1445–1453. - PubMed
-
- Heilmann C. Adhesion mechanisms of staphylococci. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;715:105–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

