Simultaneous bactericidal and osteogenic effect of nanoparticulate calcium phosphate powders loaded with clindamycin on osteoblasts infected with Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 24582242
- PMCID: PMC3942787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.01.008
Simultaneous bactericidal and osteogenic effect of nanoparticulate calcium phosphate powders loaded with clindamycin on osteoblasts infected with Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
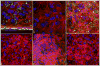
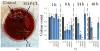
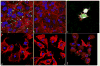
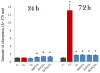
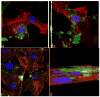
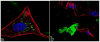
Staphylococcus aureus internalized by bone cells and shielded from the immune system provides a reservoir of bacteria in recurring osteomyelitis. Its targeting by the antibiotic therapy may thus be more relevant for treating chronic bone infection than eliminating only the pathogens colonizing the bone matrix. Assessed was the combined osteogenic and antibacterial effect of clindamycin-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles of different monophasic compositions on co-cultures comprising osteoblasts infected with S. aureus. Antibiotic-carrying particles were internalized by osteoblasts and minimized the concentration of intracellular bacteria. In vitro treatments of the infected cells, however, could not prevent cell necrosis due to the formation of toxic byproducts of the degradation of the bacterium. Antibiotic-loaded particles had a positive morphological effect on osteoblasts per se, without reducing their viability, alongside stimulating the upregulation of expression of different bone growth markers in infected osteoblasts to a higher degree than achieved during the treatment with antibiotic only.
Keywords: Calcium phosphate; Controlled drug delivery; Nanoparticles; Osteogenesis; Osteomyelitis; Staphylococcus aureus.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

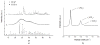


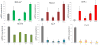
References
-
- Bisland SK, Chien C, Wilson BC, Burch S. Photochem Photobio Sci. 2006;5:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Bone Health and Osteoporosis: A Report of the Surgeon General. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; Rockville, MD: 2004. - PubMed
-
- Paluska SA. Clin Fam Practice. 2004;6:127–156.
-
- King RW, Johnson DL. Stearns DA, Talavera F, Weiss EL, Halamka JD, Kulkarni R, editors. Osteomyelitis: eMedicine Medscape Reference. 2011 retrieved from http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/785020-overview#a0101.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

