Mastocytosis associated with a rare germline KIT K509I mutation displays a well-differentiated mast cell phenotype
- PMID: 24582309
- PMCID: PMC4125511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.12.1090
Mastocytosis associated with a rare germline KIT K509I mutation displays a well-differentiated mast cell phenotype
Abstract
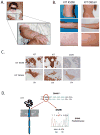
Background: Mastocytosis associated with germline KIT activating mutations is exceedingly rare. We report the unique clinicopathologic features of a patient with systemic mastocytosis caused by a de novo germline KIT K509I mutation.
Objectives: We sought to investigate the effect of the germline KIT K509I mutation on human mast cell development and function.
Methods: Primary human mast cells derived from CD34(+) peripheral blood progenitors were examined for growth, development, survival, and IgE-mediated activation. In addition, a mast cell transduction system that stably expressed the KIT K509I mutation was established.
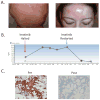
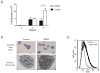
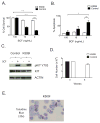
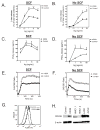
Results: KIT K509I biopsied mast cells were round, CD25(-), and well differentiated. KIT K509I progenitors cultured in stem cell factor (SCF) demonstrated a 10-fold expansion compared with progenitors from healthy subjects and developed into mature hypergranular mast cells with enhanced antigen-mediated degranulation. KIT K509I progenitors cultured in the absence of SCF survived but lacked expansion and developed into hypogranular mast cells. A KIT K509I mast cell transduction system revealed SCF-independent survival to be reliant on the preferential splicing of KIT at the adjacent exonic junction.
Conclusion: Germline KIT mutations associated with mastocytosis drive a well-differentiated mast cell phenotype distinct to that of somatic KIT D816V disease, the oncogenic potential of which might be influenced by SCF and selective KIT splicing.
Keywords: K509I; KIT; germline; mast cells; mastocytosis; well differentiated.
Published by Mosby, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
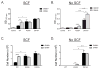
References
-
- Horny H-P, Metcalfe DD, Bennett JM, Bain BJ, Akin C, Escribano L, Valent P. Mastocytosis. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffee ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Varderman JW, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008. pp. 54–63.
-
- Valent P, Horny HP, Escribano L, Longley BJ, Li CY, Schwartz LB, et al. Diagnostic criteria and classification of mastocytosis: a consensus proposal. Leuk Res. 2001;25(7):603–25. - PubMed
-
- Nagata H, Okada T, Worobec AS, Semere T, Metcalfe DD. c-kit mutation in a population of patients with mastocytosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997;113(1–3):184–6. - PubMed
-
- Beghini A, Tibiletti MG, Roversi G, Chiaravalli AM, Serio G, Capella C, et al. Germline mutation in the juxtamembrane domain of the kit gene in a family with gastrointestinal stromal tumors and urticaria pigmentosa. Cancer. 2001;92(3):657–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

