Modulation of HCN channels in lateral septum by nicotine
- PMID: 24582613
- PMCID: PMC5384640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.02.012
Modulation of HCN channels in lateral septum by nicotine
Abstract
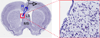
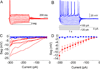
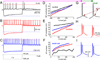
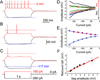
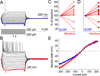
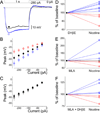
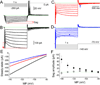
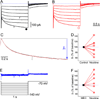
The effects of addictive drugs most commonly occur via interactions with target receptors. The same is true of nicotine and its multiple receptors in a variety of cell types. However, there are also side effects for given substances that can dramatically change cellular, tissue, organ, and organism functions. In this study, we present evidence that nicotine possesses such properties, and modulates neuronal excitability. We recorded whole-cell voltages and currents in neurons situated in the dorsal portion of the lateral septum in acute coronal brain slices of adult rats. Our experiments in the lateral septum revealed that nicotine directly affects HCN - hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated non-selective cation channels. We demonstrate that nicotine effects persist despite the concurrent application of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors' antagonists - mecamylamine, methyllycaconitine, and dihydro-β-erythroidine. These results are novel in regard to HCN channels in the septum, in general, and in their sensitivity to nicotine, in particular.
Keywords: Action potentials; HCN channels; Sag potential; Septal neurons; h-Current.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

