Germline quality control: eEF2K stands guard to eliminate defective oocytes
- PMID: 24582807
- PMCID: PMC4712648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.01.027
Germline quality control: eEF2K stands guard to eliminate defective oocytes
Abstract
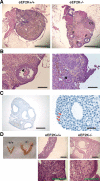
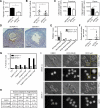
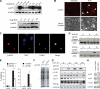
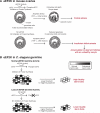
The control of germline quality is critical to reproductive success and survival of a species; however, the mechanisms underlying this process remain unknown. Here, we demonstrate that elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K), an evolutionarily conserved regulator of protein synthesis, functions to maintain germline quality and eliminate defective oocytes. We show that disruption of eEF2K in mice reduces ovarian apoptosis and results in the accumulation of aberrant follicles and defective oocytes at advanced reproductive age. Furthermore, the loss of eEF2K in Caenorhabditis elegans results in a reduction of germ cell death and significant decline in oocyte quality and embryonic viability. Examination of the mechanisms by which eEF2K regulates apoptosis shows that eEF2K senses oxidative stress and quickly downregulates short-lived antiapoptotic proteins, XIAP and c-FLIPL by inhibiting global protein synthesis. These results suggest that eEF2K-mediated inhibition of protein synthesis renders cells susceptible to apoptosis and functions to eliminate suboptimal germ cells.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ablation of elongation factor 2 kinase enhances heat-shock protein 90 chaperone expression and protects cells under proteotoxic stress.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 3;294(18):7169-7176. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC119.008036. Epub 2019 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30890561 Free PMC article.
-
Binucleate germ cells in Caenorhabditis elegans are removed by physiological apoptosis.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 19;14(7):e1007417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007417. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30024879 Free PMC article.
-
BCL2-modifying factor promotes germ cell loss during murine oogenesis.Reproduction. 2016 May;151(5):553-62. doi: 10.1530/REP-15-0561. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Reproduction. 2016. PMID: 26917450
-
Eukaryotic Elongation Factor 2 Kinase a Pharmacological Target to Regulate Protein Translation Dysfunction in Neurological Diseases.Neuroscience. 2020 Oct 1;445:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.02.015. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Neuroscience. 2020. PMID: 32088293 Review.
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase as a drug target in cancer, and in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Mar;37(3):285-94. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.123. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26806303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation and Signal Transduction Pathways in Translational Control.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Jul 1;11(7):a033050. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033050. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 29959191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-individual purifying selection on mitochondrial DNA variants during human oogenesis.Hum Reprod. 2017 May 1;32(5):1100-1107. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex051. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28333293 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of eEF2 kinase improves deficits in novel object recognition memory in aged mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2020 Nov;95:154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.07.016. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Neurobiol Aging. 2020. PMID: 32810756 Free PMC article.
-
MYCBP interacts with Sakura and Otu and is essential for germline stem cell renewal and differentiation and oogenesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 2:2025.07.01.662550. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.01.662550. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Jul 15;13:RP103828. doi: 10.7554/eLife.103828. PMID: 40631179 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Inhibition of eEF2K synergizes with glutaminase inhibitors or 4EBP1 depletion to suppress growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9181. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88816-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33911160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browne GJ, Proud CG. Regulation of peptide-chain elongation in mammalian cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002;269:5360–5368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03TW008217/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019890/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AI078513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 TW008217/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM085282/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM057300/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1AI078513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM57300/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG19890/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA81102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG042870/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG042870/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM078195/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
