Inhibitors of NF-kappaB reverse cellular invasion and target gene upregulation in an experimental model of aggressive oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24582884
- PMCID: PMC4001858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.02.004
Inhibitors of NF-kappaB reverse cellular invasion and target gene upregulation in an experimental model of aggressive oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is diagnosed in 640,000 patients yearly with a poor (50%) 5-year survival rate that has not changed appreciably in decades.
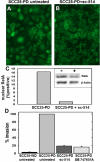
Paitents and methods: To investigate molecular changes that drive OSCC progression, cDNA microarray analysis was performed using human OSCC cells that form aggressive poorly differentiated tumors (SCC25-PD) in a murine orthotopic xenograft model compared to cells that produce well-differentiated tumors (SCC25-WD).
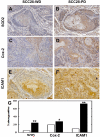
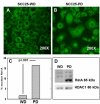
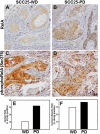
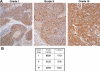
Results: As this analysis revealed that 59 upregulated genes were NF-κB target genes, the role of NF-κB activation in alteration of the transcriptional profile was evaluated. The mRNA and protein upregulation of a panel NF-κB target genes was validated by real-time qPCR and immunohistochemistry. Additionally, nuclear translocation of RelA was greatly increased in SCC25-PD, increased nuclear RelA was observed in oral tumors initiated with SCC25-PD compared with tumors initiated by SCC25-WD, and nuclear RelA correlated with stage of disease on two human OSCC tissue microarrays. Treatment of SCC25-PD cells with the IKKβ-inhibitor sc-514, that effectively prevents RelA phosphorylation on Ser 536, reversed nuclear-translocation of RelA and strongly inhibited NF-κB gene activation. Furthermore, blocking the phosphorylation of RelA using the MSK1/2 inhibitor SB 747651A significantly reduced the mRNA upregulation of a subset of target genes. Treatment with sc-514 or SB747651A markedly diminished cellular invasiveness.
Conclusions: These studies support a model wherein NF-κB is constitutively active in aggressive OSCC, while blocking the NF-κB pathway reduces NF-κB target gene upregulation and cellular invasiveness.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry; Invasion; NF-kappaB (NF-κB); Oral cancer; Transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Sano D, Myers JN. Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Can. Met. Rev. 2007;26(3-4):645–62. - PubMed
-
- Rusthoven K, Ballonoff A, Raben D, Chen C. Poor prognosis in patients with stage I and II oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2008;112(2):345–51. - PubMed
-
- Myers JN, Holsinger FC, Jasser SA, Bekele BN, Fidler IJ. An orthotopic nude mouse model of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:293–8. - PubMed
-
- Ziober AF, Patel KR, Alawi F, Gimotty P, Weber RS, Feldman MM, Chalian AA, Weinstein GS, Hunt J, Ziober BL. Identification of a gene signature for rapid screening of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(20 Pt 1):5960–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

