Secretin stimulates biliary cell proliferation by regulating expression of microRNA 125b and microRNA let7a in mice
- PMID: 24583060
- PMCID: PMC4035389
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.02.030
Secretin stimulates biliary cell proliferation by regulating expression of microRNA 125b and microRNA let7a in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: Proliferating cholangiocytes secrete and respond to neuroendocrine hormones, including secretin. We investigated whether secretin secreted by S cells and cholangiocytes stimulates biliary proliferation in mice.
Methods: Cholestasis was induced in secretin knockout (Sct(-/-)) and wild-type (control) mice by bile duct ligation (BDL). At days 3 and 7 after BDL, control and Sct(-/-) mice received tail-vein injections of morpholinos against microRNA 125b or let7a. One week later, liver tissues and cholangiocytes were collected. Immunohistochemical, immunoblot, luciferase reporter, and real-time polymerase chain reaction assays were performed. Intrahepatic bile duct mass (IBDM) and proliferation were measured. Secretin secretion was measured in conditioned media from cholangiocytes and S cells and in serum and bile.
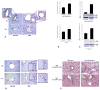
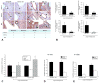
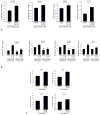
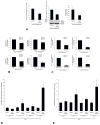
Results: Secretin secretion was increased in supernatants from cholangiocytes and S cells and in serum and bile after BDL in control mice. BDL Sct(-/-) mice had lower IBDM, reduced proliferation, and reduced production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) A and nerve growth factor (NGF) compared with BDL control. BDL and control mice given morpholinos against microRNA 125b or let7a had increased IBDM. Livers of mice given morpholinos against microRNA 125b had increased expression of VEGFA, and those treated with morpholinos against microRNA let7a had increased expression of NGF. Secretin regulated VEGF and NGF expression that negatively correlated with microRNA 125b and let7a levels in liver tissue.
Conclusions: After liver injury, secretin produced by cholangiocytes and S cells reduces microRNA 125b and let7a levels, resulting in up-regulation of VEGF and NGF. Modulation of cholangiocyte expression of secretin could be a therapeutic approach for biliary diseases.
Keywords: Biliary Epithelium; Gastrointestinal Hormones; Heterogeneity; cAMP.
Copyright © 2014 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockout of secretin receptor reduces large cholangiocyte hyperplasia in mice with extrahepatic cholestasis induced by bile duct ligation.Hepatology. 2010 Jul;52(1):204-14. doi: 10.1002/hep.23657. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20578263 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of histidine decarboxylase decreases bile duct ligation-induced biliary hyperplasia via downregulation of the histidine decarboxylase/VEGF axis through PKA-ERK1/2 signaling.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):G813-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00188.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25169977
-
The secretin/secretin receptor axis modulates liver fibrosis through changes in transforming growth factor-β1 biliary secretion in mice.Hepatology. 2016 Sep;64(3):865-79. doi: 10.1002/hep.28622. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 27115285 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of cholangiocyte responses to injury.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Apr;1864(4 Pt B):1262-1269. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.06.017. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 28648950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholangiocytes and blood supply.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jun 14;12(22):3546-52. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i22.3546. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16773711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of the Tryptophan Hydroxylase 1/Monoamine Oxidase-A/5-Hydroxytryptamine/5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2A/2B/2C Axis Regulates Biliary Proliferation and Liver Fibrosis During Cholestasis.Hepatology. 2020 Mar;71(3):990-1008. doi: 10.1002/hep.30880. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 31344280 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-200c-3p targets SESN1 and represses the IL-6/AKT loop to prevent cholangiocyte activation and cholestatic liver fibrosis.Lab Invest. 2022 May;102(5):485-493. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00710-6. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Lab Invest. 2022. PMID: 34880414 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of microRNA-21 attenuates alcoholic hepatitis through the VHL/NF-κB signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):G385-G398. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00111.2018. Epub 2018 May 31. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29848019 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of microRNA-21 reduces biliary hyperplasia and liver fibrosis in cholestatic bile duct ligated mice.Lab Invest. 2016 Dec;96(12):1256-1267. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.112. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27775690 Free PMC article.
-
Regulators of Cholangiocyte Proliferation.Gene Expr. 2017 Feb 10;17(2):155-171. doi: 10.3727/105221616X692568. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Gene Expr. 2017. PMID: 27412505 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lleo A, Invernizzi P. Apotopes and innate immune system: Novel players in the primary biliary cirrhosis scenario. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45:630–6. - PubMed
-
- Lazaridis KN, Strazzabosco M, LaRusso NF. The cholangiopathies: disorders of biliary epithelia. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1565–77. - PubMed
-
- LeSage G, Glaser S, Marucci L, et al. Acute carbon tetrachloride feeding induces damage of large but not small cholangiocytes from BDL rat liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1999;276:G1289–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

