Role of the kappa-opioid receptor system in stress-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking in rats
- PMID: 24583188
- PMCID: PMC4082245
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.029
Role of the kappa-opioid receptor system in stress-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking in rats
Abstract
Rationale: The correlation between stress and smoking is well established. The mechanisms that underlie this relationship are, however, unclear. Recent data suggest that the kappa-opioid system is involved in the mediation of negative affective states associated with stress thereby promoting drug addiction and relapse. Pharmacological treatments targeting the kappa-opioid system and this mechanism may prove to be useful therapeutics for nicotine addiction in the future.
Objectives: We sought to determine whether there was a stress-specific role of the kappa-opioid system in nicotine seeking behavior.
Method: Groups of male Long Evans rats were trained to self-administer nicotine intravenously; their operant responding for nicotine was extinguished prior to tests of reinstatement. Pretreatment with systemic injections of the kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) antagonist nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) was given prior to tests of stress (systemic injections of yohimbine (YOH)) or cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking. Systemic injections of the KOR agonist U50,488 were also given in a test for reinstatement of nicotine seeking.
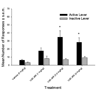
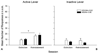
Results: Nor-BNI pretreatment at 1h and 24h prior to testing was able to block YOH-induced, but not cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking. U50,488 reinstated nicotine seeking behavior in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusions: These findings support the hypothesis that the kappa-opioid system is involved in relapse to nicotine seeking induced by stress, but not by conditioned cues. KOR antagonists such as nor-BNI may therefore be useful novel therapeutic agents for decreasing the risk of stress-induced drug relapse.
Keywords: Nicotine; Nor-binaltorphimine; Reinstatement; Stress; U50,488; Yohimbine.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of kappa opioid receptors in stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking in rats.Brain Behav. 2014 May;4(3):356-67. doi: 10.1002/brb3.222. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Brain Behav. 2014. PMID: 24944865 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Nicotine Preference Requires Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid Activity in the Basolateral Amygdala.J Neurosci. 2016 Sep 21;36(38):9937-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0953-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27656031 Free PMC article.
-
A single, extinction-based treatment with a kappa opioid receptor agonist elicits a long-term reduction in cocaine relapse.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jun;43(7):1492-1497. doi: 10.1038/s41386-017-0006-4. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29472645 Free PMC article.
-
Translational and reverse translational research on the role of stress in drug craving and relapse.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Nov;218(1):69-82. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2263-y. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21494792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuropharmacology of relapse to food seeking: methodology, main findings, and comparison with relapse to drug seeking.Prog Neurobiol. 2009 Sep;89(1):18-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 Jun 2. Prog Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19497349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel approaches for the treatment of psychostimulant and opioid abuse - focus on opioid receptor-based therapies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014 Nov;9(11):1333-44. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.964203. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25253272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kappa-opioid receptor activation reinstates nicotine self-administration in mice.Addict Neurosci. 2022 Jun;2:100017. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100017. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Addict Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36118179 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Paradoxical changes in brain reward status during oxycodone self-administration in a novel test of the negative reinforcement hypothesis.Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Sep;178(18):3797-3812. doi: 10.1111/bph.15520. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33948939 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of the kappa opioid receptor attenuates THC-induced place aversions in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017 Dec;163:30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017. PMID: 29100992 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine and opioid co-dependence: Findings from bench research to clinical trials.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Mar;134:104507. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.12.030. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34968525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264(1):489–495. - PubMed
-
- Beardsley PM, Howard JL, Shelton KL, Carroll FI. Differential effects of the novel kappa opioid receptor antagonist, JDTic, on reinstatement of cocaine-seeking induced by foot shock stressors vs. cocaine primes and its antidepressant-like effects in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;183(1):118–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

