Induction of human plasmablasts during infection with antibiotic-resistant nosocomial bacteria
- PMID: 24583361
- PMCID: PMC4054983
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dku047
Induction of human plasmablasts during infection with antibiotic-resistant nosocomial bacteria
Abstract
Objectives: Nosocomial pathogens such as Acinetobacter baumannii are a growing public health threat, due in part to their increasing resistance to antibiotics. Since some strains are resistant to all available antibiotics, novel therapies are urgently needed. Plasmablasts are short-lived B cells found in the blood that can be collected and harnessed to produce therapeutic antibodies. We set out to determine whether plasmablasts are induced during infection with A. baumannii and other nosocomial pathogens.
Methods: We obtained blood samples from patients infected with antibiotic-resistant nosocomial pathogens, and analysed their plasmablast response by flow cytometry.
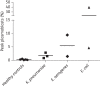
Results: We observed a strong induction of plasmablasts in patients with antibiotic-resistant A. baumannii infection. Furthermore, plasmablasts were also induced in response to other drug-resistant nosocomial pathogens.
Conclusions: These data suggest that plasmablasts may be broadly harnessed to develop therapeutic antibodies to combat otherwise untreatable antibiotic-resistant infections.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; antibody therapy; nosocomial infections.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Rice LB. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: no ESKAPE. J Infect Dis. 2008;197:1079–81. - PubMed
-
- Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:268–81. - PubMed
-
- White AR. Effective antibacterials: at what cost? The economics of antibacterial resistance and its control. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:1948–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

