Phase I dendritic cell p53 peptide vaccine for head and neck cancer
- PMID: 24583792
- PMCID: PMC4017234
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2617
Phase I dendritic cell p53 peptide vaccine for head and neck cancer
Abstract
Background: p53 accumulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells creates a targetable tumor antigen. Adjuvant dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccination against p53 was tested in a phase I clinical trial.
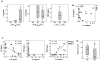
Experimental methods: Monocyte-derived DC from 16 patients were loaded with two modified HLA-class I p53 peptides (Arm 1), additional Th tetanus toxoid peptide (Arm 2), or additional Th wild-type (wt) p53-specific peptide (Arm 3). Vaccine DCs (vDC) were delivered to inguinal lymph nodes at three time points. vDC phenotype, circulating p53-specific T cells, and regulatory T cells (Treg) were serially monitored by flow cytometry and cytokine production by Luminex. vDC properties were compared with those of DC1 generated with an alternative maturation regimen.
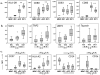
Results: No grade II-IV adverse events were observed. Two-year disease-free survival of 88% was favorable. p53-specific T-cell frequencies were increased postvaccination in 11 of 16 patients (69%), with IFN-γ secretion detected in four of 16 patients. Treg frequencies were consistently decreased (P = 0.006) relative to prevaccination values. The phenotype and function of DC1 were improved relative to vDC.
Conclusion: Adjuvant p53-specific vaccination of patients with HNSCC was safe and associated with promising clinical outcome, decreased Treg levels, and modest vaccine-specific immunity. HNSCC patients' DC required stronger maturation stimuli to reverse immune suppression and improve vaccine efficacy.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: none
Figures


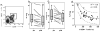
References
-
- Whiteside TL, Stanson J, Shurin MR, Ferrone S. Antigen-processing machinery in human dendritic cells: up-regulation by maturation and down-regulation by tumor cells. Journal of immunology. 2004;173(3):1526–34. - PubMed
-
- Strauss L, Bergmann C, Whiteside TL. Functional and phenotypic characteristics of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ Treg clones obtained from peripheral blood of patients with cancer. International journal of cancer. 2007;121(11):2473–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

