Preclinical and early clinical evaluation of the oral AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia
- PMID: 24583795
- PMCID: PMC3989412
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1978
Preclinical and early clinical evaluation of the oral AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: Recent studies suggested that AKT activation might confer poor prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), providing the rationale for therapeutic targeting of this signaling pathway. We, therefore, explored the preclinical and clinical anti-AML activity of an oral AKT inhibitor, MK-2206. Experimental Methods: We first studied the effects of MK-2206 in human AML cell lines and primary AML specimens in vitro. Subsequently, we conducted a phase II trial of MK-2206 (200 mg weekly) in adults requiring second salvage therapy for relapsed/refractory AML, and assessed target inhibition via reverse phase protein array (RPPA).
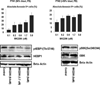
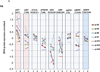
Results: In preclinical studies, MK-2206 dose-dependently inhibited growth and induced apoptosis in AML cell lines and primary AML blasts. We then treated 19 patients with MK-2206 but, among 18 evaluable participants, observed only 1 (95% confidence interval, 0%-17%) response (complete remission with incomplete platelet count recovery), leading to early study termination. The most common grade 3/4 drug-related toxicity was a pruritic rash in 6 of 18 patients. Nevertheless, despite the use of MK-2206 at maximum tolerated doses, RPPA analyses indicated only modest decreases in Ser473 AKT (median 28%; range, 12%-45%) and limited inhibition of downstream targets.
Conclusions: Although preclinical activity of MK-2206 can be demonstrated, this inhibitor has insufficient clinical antileukemia activity when given alone at tolerated doses, and alternative approaches to block AKT signaling should be explored.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01253447.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MK-2206 induces apoptosis of AML cells and enhances the cytotoxicity of cytarabine.Med Oncol. 2015 Jul;32(7):206. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0650-7. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26087957
-
Effects of an oral allosteric AKT inhibitor (MK-2206) on human nasopharyngeal cancer in vitro and in vivo.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Oct 10;8:1827-37. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S67961. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25336925 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of AKT with the orally active allosteric AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to progestin.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041593. Epub 2012 Jul 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911820 Free PMC article.
-
First-in-man clinical trial of the oral pan-AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in patients with advanced solid tumors.J Clin Oncol. 2011 Dec 10;29(35):4688-95. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.35.5263. Epub 2011 Oct 24. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22025163 Clinical Trial.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin module for acute myelogenous leukemia therapy: from bench to bedside.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(19):2009-23. doi: 10.2174/092986707781368423. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17691943 Review.
Cited by
-
PI3K Targeting in Non-solid Cancer.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022;436:393-407. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06566-8_17. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36243854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caspase-2 is essential for proliferation and self-renewal of nucleophosmin-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.Sci Adv. 2024 Aug 2;10(31):eadj3145. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj3145. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39093977 Free PMC article.
-
Akt inhibition synergizes with polycomb repressive complex 2 inhibition in the treatment of multiple myeloma.Cancer Sci. 2019 Dec;110(12):3695-3707. doi: 10.1111/cas.14207. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31571328 Free PMC article.
-
Akt inhibitors in cancer treatment: The long journey from drug discovery to clinical use (Review).Int J Oncol. 2016 Mar;48(3):869-85. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3306. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26698230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MK-2206 induces apoptosis of AML cells and enhances the cytotoxicity of cytarabine.Med Oncol. 2015 Jul;32(7):206. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0650-7. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26087957
References
-
- Estey E, Döhner H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2006;368:1894–1907. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Büchner T, Burnett AK, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115:453–474. - PubMed
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296:1655–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

