Prevalence and clinical implications of epstein-barr virus infection in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries
- PMID: 24583797
- PMCID: PMC4014309
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3157
Prevalence and clinical implications of epstein-barr virus infection in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries
Erratum in
- Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 15;20(18):4974. Dybaer, Karen [corrected to Dybkaer, Karen]
Abstract
Purpose: Epstein-Barr virus-positive (EBV(+)) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of the elderly is a variant of DLBCL with worse outcome that occurs most often in East-Asian countries and is uncommon in the Western hemisphere. We studied the largest cohort of EBV(+) DLBCL, independent of age, treated with rituximab combined with CHOP (R-CHOP) in developed Western countries.
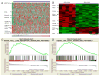
Experimental design: A large cohort (n = 732) of patients with DLBCL treated with R-CHOP chemotherapy is included from the multicenter consortium. This study group has been studied for expression of different biomarkers by immunohistochemistry, genetic abnormalities by FISH and mutation analysis, genomic information by gene expression profiling (GEP), and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA).
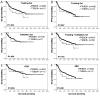
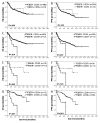
Results: Twenty-eight patients (4.0%) were positive for EBV with a median age of 60.5 years. No clinical characteristics distinguished patients with EBV(+) DLBCL from patients with EBV-negative (EBV(-)) DLBCL. Genetic aberrations were rarely seen. NF-κB p50, phosphorylated STAT-3, and CD30 were more commonly expressed in EBV(+) DLBCLs (P < 0.05). Significant differences in survival were not observed in patients with EBV(+) DLBCL versus EBV(-) DLBCL. However, CD30 expression combined with EBV conferred an inferior outcome. GEP showed a unique expression signature in EBV(+) DLBCL. GSEA revealed enhanced activity of the NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways independent of molecular subtype.
Conclusions: The clinical characteristics of patients with EBV(+) versus EBV(-) DLBCL are similar and EBV infection does not predict a worse outcome. EBV(+) DLBCL, however, has a unique genetic signature. CD30 expression is more common in EBV(+) DLBCL and, consistent CD30 and EBV is associated with an adverse outcome. Clin Cancer Res; 20(9); 2338-49. ©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nakamura S, Jaffe ES, Swerdlow SH, editors. EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008.
-
- Beltran BE, Morales D, Quinones P, Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN, Castillo JJ. EBV-positive diffuse large b-cell lymphoma in young immunocompetent individuals. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011;11:512–6. - PubMed
-
- Wada N, Ikeda J, Hori Y, Fujita S, Ogawa H, Soma T, et al. Epstein-barr virus in diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma in immunocompetent patients in Japan is as low as in Western Countries. J Med Virol. 2011;83:317–21. - PubMed
-
- Park S, Lee J, Ko YH, Han A, Jun HJ, Lee SC, et al. The impact of Epstein-Barr virus status on clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2007;110:972–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

