CTLA4 blockade broadens the peripheral T-cell receptor repertoire
- PMID: 24583799
- PMCID: PMC4008652
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2648
CTLA4 blockade broadens the peripheral T-cell receptor repertoire
Erratum in
-
Correction: CTLA4 Blockade Broadens the Peripheral T-cell Receptor Repertoire.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jul 15;21(14):3359. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1088. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26180060 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the immunomodulatory effects of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA4) blockade with tremelimumab in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC).
Experimental design: We used next-generation sequencing to study the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) from the rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) variable beta (V-beta) in PBMCs of 21 patients, at baseline and 30 to 60 days after receiving tremelimumab.
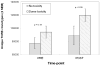
Results: After receiving tremelimumab, there was a median of 30% increase in unique productive sequences of TCR V-beta CDR3 in 19 out of 21 patients, and a median decrease of 30% in only 2 out of 21 patients. These changes were significant for richness (P = 0.01) and for Shannon index diversity (P = 0.04). In comparison, serially collected PBMCs from four healthy donors did not show a significant change in TCR V-beta CDR3 diversity over 1 year. There was a significant difference in the total unique productive TCR V-beta CDR3 sequences between patients experiencing toxicity with tremelimumab compared with patients without toxicity (P = 0.05). No relevant differences were noted between clinical responders and nonresponders.
Conclusions: CTLA4 blockade with tremelimumab diversifies the peripheral T-cell pool, representing a pharmacodynamic effect of how this class of antibodies modulates the human immune system.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The rest of the co-authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
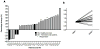


References
-
- Camacho LH, Antonia S, Sosman J, Kirkwood JM, Gajewski TF, Redman B, et al. Phase I/II trial of tremelimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2009;27(7):1075–81. - PubMed
-
- Sanderson K, Scotland R, Lee P, Liu D, Groshen S, Snively J, et al. Autoimmunity in a phase I trial of a fully human anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 monoclonal antibody with multiple melanoma peptides and Montanide ISA 51 for patients with resected stages III and IV melanoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(4):741–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

