Astrocytic laminin regulates pericyte differentiation and maintains blood brain barrier integrity
- PMID: 24583950
- PMCID: PMC3992931
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4413
Astrocytic laminin regulates pericyte differentiation and maintains blood brain barrier integrity
Abstract
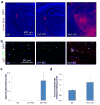
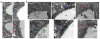
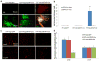
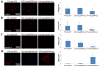
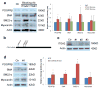
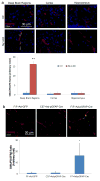
Blood brain barrier (BBB) breakdown is not only a consequence of but also contributes to many neurological disorders, including stroke and Alzheimer's disease. How the basement membrane (BM) contributes to the normal functioning of the BBB remains elusive. Here we use conditional knockout mice and an acute adenovirus-mediated knockdown model to show that lack of astrocytic laminin, a brain-specific BM component, induces BBB breakdown. Using functional blocking antibody and RNAi, we further demonstrate that astrocytic laminin, by binding to integrin α2 receptor, prevents pericyte differentiation from the BBB-stabilizing resting stage to the BBB-disrupting contractile stage, and thus maintains the integrity of BBB. Additionally, loss of astrocytic laminin decreases aquaporin-4 (AQP4) and tight junction protein expression. Altogether, we report a critical role for astrocytic laminin in BBB regulation and pericyte differentiation. These results indicate that astrocytic laminin maintains the integrity of BBB through, at least in part, regulation of pericyte differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Persidsky Y, Ramirez SH, Haorah J, Kanmogne GD. Blood-brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006;1:223–236. - PubMed
-
- Zipser BD, et al. Microvascular injury and blood-brain barrier leakage in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:977–986. - PubMed
-
- van Vliet EA, et al. Blood-brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain. 2007;130:521–534. - PubMed
-
- Wardlaw JM, et al. Lacunar stroke is associated with diffuse blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:194–202. - PubMed
-
- Guillemin GJ, Brew BJ. Microglia, macrophages, perivascular macrophages, and pericytes: a review of function and identification. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:388–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

