Dual kinase-bromodomain inhibitors for rationally designed polypharmacology
- PMID: 24584101
- PMCID: PMC3998711
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1471
Dual kinase-bromodomain inhibitors for rationally designed polypharmacology
Erratum in
- Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Aug;10(8):692
Abstract
Concomitant inhibition of multiple cancer-driving kinases is an established strategy to improve the durability of clinical responses to targeted therapies. The difficulty of discovering kinase inhibitors with an appropriate multitarget profile has, however, necessitated the application of combination therapies, which can pose major clinical development challenges. Epigenetic reader domains of the bromodomain family have recently emerged as new targets for cancer therapy. Here we report that several clinical kinase inhibitors also inhibit bromodomains with therapeutically relevant potencies and are best classified as dual kinase-bromodomain inhibitors. Nanomolar activity on BRD4 by BI-2536 and TG-101348, which are clinical PLK1 and JAK2-FLT3 kinase inhibitors, respectively, is particularly noteworthy as these combinations of activities on independent oncogenic pathways exemplify a new strategy for rational single-agent polypharmacological targeting. Furthermore, structure-activity relationships and co-crystal structures identify design features that enable a general platform for the rational design of dual kinase-bromodomain inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
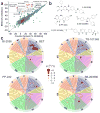
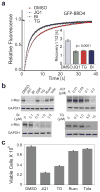
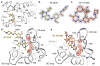
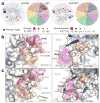

Comment in
-
Drug discovery: follow your lead.Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Apr;10(4):244-5. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1484. Nat Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24643239 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Haber DA, Gray NS, Baselga J. The evolving war on cancer. Cell. 2011;145:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Trusolino L, Bertotti A. Compensatory pathways in oncogenic kinase signaling and resistance to targeted therapies: six degrees of separation. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Davis MI, et al. Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:1046–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

