Dopamine D3 receptor is necessary for ethanol consumption: an approach with buspirone
- PMID: 24584330
- PMCID: PMC4059912
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2014.51
Dopamine D3 receptor is necessary for ethanol consumption: an approach with buspirone
Abstract
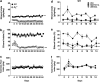
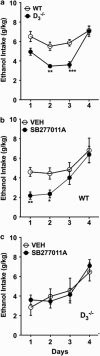
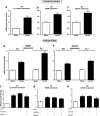
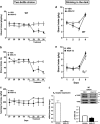
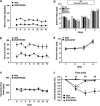
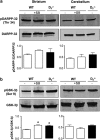
Mesolimbic dopamine (DA) controls drug- and alcohol-seeking behavior, but the role of specific DA receptor subtypes is unclear. We tested the hypothesis that D3R gene deletion or the D3R pharmacological blockade inhibits ethanol preference in mice. D3R-deficient mice (D3R(-/-)) and their wild-type (WT) littermates, treated or not with the D3R antagonists SB277011A and U99194A, were tested in a long-term free choice ethanol-drinking (two-bottle choice) and in a binge-like ethanol-drinking paradigm (drinking in the dark, DID). The selectivity of the D3R antagonists was further assessed by molecular modeling. Ethanol intake was negligible in D3R(-/-) and robust in WT both in the two-bottle choice and DID paradigms. Treatment with D3R antagonists inhibited ethanol intake in WT but was ineffective in D3R(-/-) mice. Ethanol intake increased the expression of RACK1 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in both WT and D3R(-/-); in WT there was also a robust overexpression of D3R. Thus, increased expression of D3R associated with activation of RACK1/BDNF seems to operate as a reinforcing mechanism in voluntary ethanol intake. Indeed, blockade of the BDNF pathway by the TrkB selective antagonist ANA-12 reversed chronic stable ethanol intake and strongly decreased the striatal expression of D3R. Finally, we evaluated buspirone, an approved drug for anxiety disorders endowed with D3R antagonist activity (confirmed by molecular modeling analysis), that resulted effective in inhibiting ethanol intake. Thus, DA signaling via D3R is essential for ethanol-related reward and consumption and may represent a novel therapeutic target for weaning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The dopamine D3 receptor is part of a homeostatic pathway regulating ethanol consumption.J Neurosci. 2006 Feb 1;26(5):1457-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3786-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16452669 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D3 receptor-dependent changes in alpha6 GABAA subunit expression in striatum modulate anxiety-like behaviour: Responsiveness and tolerance to diazepam.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Sep;25(9):1427-36. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2014.11.004. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25482686
-
Lentiviral vector-mediated dopamine d3 receptor modulation in the rat brain impairs alcohol intake and ethanol-induced conditioned place preference.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Sep;38(9):2369-76. doi: 10.1111/acer.12503. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 25257287
-
Current drug treatments targeting dopamine D3 receptor.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;165:164-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27343365 Review.
-
Targeting the dopamine D3 receptor: an overview of drug design strategies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Jul;11(7):641-64. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1185413. Epub 2016 May 30. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27135354 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade Attenuates Methamphetamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion and Neurotoxicity.Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Apr;15(2):500-510. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0613-8. Neurotherapeutics. 2018. PMID: 29464572 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal circuitry underlying the impact of D3 receptor ligands in drug addiction.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Sep;25(9):1401-9. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2014.08.017. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25266821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and addiction: Pathological versus therapeutic effects on drug seeking.Brain Res. 2015 Dec 2;1628(Pt A):68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.058. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25451116 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Anxiolytic Drug Buspirone Using CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglial Cells.Cells. 2021 May 25;10(6):1312. doi: 10.3390/cells10061312. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34070429 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of miR-15a-5p, miR-497a-5p and miR-511-5p Is Associated with Modulation of BDNF and FKBP5 in Brain Areas of PTSD-Related Susceptible and Resilient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 13;22(10):5157. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105157. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG. The Akt-GSK-3 signaling cascade in the actions of dopamine. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28:166–172. - PubMed
-
- Bouthenet ML, Souil E, Martres MP, Sokoloff P, Giros B, Schwartz JC. Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res. 1991;564:203–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

