Sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, acutely inhibits intestinal lipoprotein particle secretion in healthy humans
- PMID: 24584549
- PMCID: PMC4066342
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-1654
Sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, acutely inhibits intestinal lipoprotein particle secretion in healthy humans
Abstract
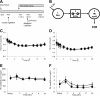
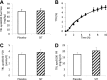
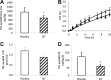
The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin, an antidiabetic agent, which lowers blood glucose levels, also reduces postprandial lipid excursion after a mixed meal. The underlying mechanism of this effect, however, is not clear. This study examined the production and clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particles from the liver and intestine in healthy volunteers in response to a single oral dose of sitagliptin. Using stable isotope tracer techniques and with control of pancreatic hormone levels, the kinetics of lipoprotein particles of intestinal and hepatic origin were measured. Compared with placebo, sitagliptin decreased intestinal lipoprotein concentration by inhibiting particle production, independent of changes in pancreatic hormones, and circulating levels of glucose and free fatty acids. Fractional clearance of particles of both intestinal and hepatic origin, and production of particles of hepatic origin, were not affected. This pleiotropic effect of sitagliptin may explain the reduction in postprandial lipemia seen in clinical trials of this agent and may provide metabolic benefits beyond lowering of glucose levels.
© 2014 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Juutilainen A, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T, Pyörälä K, Laakso M. Type 2 diabetes as a “coronary heart disease equivalent”: an 18-year prospective population-based study in Finnish subjects. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2901–2907 - PubMed
-
- Howard BV, Howard WJ. Dyslipidemia in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev 1994;15:263–274 - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Benn M, Schnohr P, Tybjaerg-Hansen A. Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. JAMA 2007;298:299–308 - PubMed
-
- Bansal S, Buring JE, Rifai N, Mora S, Sacks FM, Ridker PM. Fasting compared with nonfasting triglycerides and risk of cardiovascular events in women. JAMA 2007;298:309–316 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

