Prognostic value of serum von Willebrand factor, but not soluble ICAM and VCAM, for mortality and cardiovascular events is independent of residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 24584618
- PMCID: PMC4269496
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2012.00004
Prognostic value of serum von Willebrand factor, but not soluble ICAM and VCAM, for mortality and cardiovascular events is independent of residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Objective: We explored associations between markers of endothelial dysfunction and outcome events, and whether those associations were independent of residual renal function (RRF) in patients on peritoneal dialysis.
Methods: The study enrolled 261 incident patients and 68 healthy control subjects who were followed till death, censoring, or study end. Demographics, biochemistry, markers of inflammation (C-reactive protein) and endothelial dysfunction [soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (sICAM), soluble vascular adhesion molecule 1 (sVCAM), and von Willebrand factor (vWf)] were examined at baseline. Outcome events included all-cause death and fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular (CV) events.
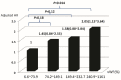
Results: Mean levels of vWf, sICAM, and sVCAM were significantly higher in patients than in healthy control subjects. Levels of sICAM and sVCAM, but not vWf, were significantly correlated with RRF. Levels of sICAM and vWf both predicted all-cause mortality and fatal and nonfatal CV events after adjustment for recognizable CV risk factors. The association between sICAM and outcome events disappeared after further adjustment for RRF. However, RRF did not change the predictive role of vWf for outcome events. Compared with the lowest vWf quartile (6.6% - 73.9%), the highest vWf quartile (240.9% - 1161%) predicted the highest risk for fatal and nonfatal CV events (adjusted hazard ratio: 2.05; 95% confidence interval: 1.15 to 3.64; p = 0.014). We observed no associations between sVCAM and RRF, or sVCAM and any outcome event.
Conclusions: The prognostic value of vWf, but not sICAM, is independent of RRF in predicting mortality and CV events.
Keywords: Cardiovascular mortality; sICAM; sVCAM; soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1; soluble vascular adhesion molecule 1; vWf; von Willebrand factor.
Copyright © 2014 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1: relationships with residual renal function, cardiac hypertrophy, and outcome of peritoneal dialysis patients.Am J Kidney Dis. 2005 Apr;45(4):715-29. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.12.012. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005. PMID: 15806475
-
Increased serum vWF and sVCAM-1 levels are associated with late or very late angiographic stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation.Coron Artery Dis. 2010 Aug;21(5):273-7. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e32833b20f1. Coron Artery Dis. 2010. PMID: 20508517
-
Elevated serum levels of soluble adhesion molecules predict death in pre-dialysis patients: association with malnutrition, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000 Oct;15(10):1624-30. doi: 10.1093/ndt/15.10.1624. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000. PMID: 11007832
-
Deciphering Endothelial Dysfunction in the HIV-Infected Population.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1134:193-215. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12668-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30919339 Review.
-
Association of soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 with mortality and adverse outcomes in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024 Oct;28(10):988-1003. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02506-6. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38678167 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inflammation and all-cause mortality in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2024 Aug 9;22:eAO0627. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2024AO0627. eCollection 2024. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39140572 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Acute Myocardial Infarction on a Disintegrin and Metalloprotease with Thrombospondin Motif 13 and Von Willebrand Factor and Their Relationship with Markers of Inflammation.Int J Vasc Med. 2020 Feb 11;2020:4981092. doi: 10.1155/2020/4981092. eCollection 2020. Int J Vasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32095288 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac risk assessment for end-stage renal disease patients on the renal transplant waiting list.Clin Kidney J. 2019 Apr 25;12(4):576-585. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfz039. eCollection 2019 Aug. Clin Kidney J. 2019. PMID: 31384451 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory activity of the coronary artery endothelial cells in conditions of the peritoneal dialysis.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):54-61. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.2023024. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35174782 Free PMC article.
-
Indoxyl sulfate - the uremic toxin linking hemostatic system disturbances with the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Jan 25;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0457-1. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28122514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Hypertension 2003; 42:1050–65. - PubMed
-
- Elsayed EF, Tighiouart H, Griffith J, Kurth T, Levey AS, Salem D, et al. Cardiovascular disease and subsequent kidney disease. Arch Intern Med 2007; 167:1130–6. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz MI, Sonmez A, Qureshi AR, Saglam M, Stenvinkel P, Yaman H, et al. Endogenous testosterone, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiovascular events in men with nondialysis chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011; 6:1617–25. - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C, Bode-Boger S, Mallamaci F, Benedetto F, Tripepi G, Malatino L, et al. Plasma concentration of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease: a prospective study. Lancet 2001; 358:2113–17. - PubMed
-
- Suliman ME, Qureshi AR, Heimbürger O, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P. Soluble adhesion molecules in end-stage renal disease: a predictor of outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21:1603–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

