Cardiovascular and mortality risk of apparent resistant hypertension in women with suspected myocardial ischemia: a report from the NHLBI-sponsored WISE Study
- PMID: 24584740
- PMCID: PMC3959684
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000660
Cardiovascular and mortality risk of apparent resistant hypertension in women with suspected myocardial ischemia: a report from the NHLBI-sponsored WISE Study
Abstract
Background: Women are more likely than men to develop resistant hypertension, which is associated with excess risk of major adverse outcomes; however, the impact of resistant hypertension in women with ischemia has not been explicitly studied. In this Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) analysis, we assessed long-term adverse outcomes associated with apparent treatment-resistant hypertension (aTRH) among women with suspected myocardial ischemia referred for coronary angiography.
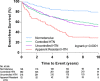
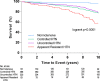
Methods and results: Women (n=927) were grouped according to baseline blood pressure (BP): normotensive (no hypertension history, BP <140/90 mm Hg, no antihypertensive drugs); controlled (BP <140/90 mm Hg and a hypertension diagnosis or on 1 to 3 drugs); uncontrolled (BP ≥140/90 mm Hg on ≤2 drugs); or aTRH (BP ≥140/90 mm Hg on 3 drugs or anyone on ≥4 drugs). Adverse outcomes (first occurrence of death [any cause], nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure or angina) were collected over 10 years of follow-up. Apparent treatment-resistant hypertension prevalence was 10.4% among those with hypertension. Women with aTRH had a greater incidence of adverse outcomes, compared with normotensive women (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.94 to 5.43), and women with controlled (HR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.26 to 2.49) and uncontrolled (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.15 to 2.27) hypertension; outcome differences were evident early in follow-up. Risk of all-cause death was greater in the aTRH group, compared to the normotensive women and women with controlled and uncontrolled hypertension.
Conclusions: In this cohort of women with evidence of ischemia, aTRH was associated with a profoundly increased long-term risk of major adverse events, including death, that emerged early during follow-up.
Keywords: WISE; hypertension; resistant hypertension; women.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality Risk Associated With Resistant Hypertension Among Women: Analysis from Three Prospective Cohorts Encompassing the Spectrum of Women's Heart Disease.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2016 Oct;25(10):996-1003. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2015.5609. Epub 2016 May 25. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2016. PMID: 27224417 Free PMC article.
-
Depression symptom severity and reported treatment history in the prediction of cardiac risk in women with suspected myocardial ischemia: The NHLBI-sponsored WISE study.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Aug;63(8):874-80. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.874. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16894063
-
Treatment-resistant hypertension and the incidence of cardiovascular disease and end-stage renal disease: results from the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT).Hypertension. 2014 Nov;64(5):1012-21. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03850. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 25259745 Clinical Trial.
-
Even "WISE-R?"-an Update on the NHLBI-Sponsored Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020 Jun 18;22(8):35. doi: 10.1007/s11883-020-00852-w. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020. PMID: 32556630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myocardial ischemia in women: lessons from the NHLBI WISE study.Clin Cardiol. 2012 Mar;35(3):141-8. doi: 10.1002/clc.21966. Clin Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22389117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of home blood pressure monitoring in resistant hypertension.Clin Hypertens. 2023 Jan 15;29(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40885-022-00226-1. Clin Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 36641498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intensive Blood Pressure Treatment for Resistant Hypertension.Hypertension. 2019 Feb;73(2):415-423. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12156. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 30580680 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to antihypertensive treatment and long-term risk: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021 Oct;23(10):1887-1896. doi: 10.1111/jch.14269. Epub 2021 Sep 21. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021. PMID: 34547175 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus paper on the evaluation and treatment of resistant hypertension by the Turkish Society of Cardiology.Anatol J Cardiol. 2020 Sep;24(3):137-152. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2020.74154. Anatol J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32870176 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of baroreflex activation therapy on cardiac function and morphology.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Oct;11(5):3360-3367. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14940. Epub 2024 Jul 5. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38970313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005; 365:217-223 - PubMed
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker‐Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Flaxman AD, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gonzalez‐Medina D, Halasa YA, Haring D, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hoen B, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Keren A, Khoo JP, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Ohno SL, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Mallinger L, March L, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGrath J, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Michaud C, Miller M, Miller TR, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Mokdad AA, Moran A, Mulholland K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nasseri K, Norman P, O'Donnell M, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Padilla RP, Perez‐Ruiz F, Perico N, Phillips D, Pierce K, Pope CA, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Raju M, Ranganathan D, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Rivara FP, Roberts T, De León FR, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Segui‐Gomez M, Shepard DS, Singh D, Singleton J, Sliwa K, Smith E, Steer A, Taylor JA, Thomas B, Tleyjeh IM, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Undurraga EA, Venketasubramanian N, Vijayakumar L, Vos T, Wagner GR, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Yip P, Zabetian A, Zheng ZJ, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012; 380:2095-2128 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sarafidis PA, Georgianos P, Bakris GL. Resistant hypertension—its identification and epidemiology. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013; 9:51-58 - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, Ferdinand K, Giles TD, Falkner B, Carey RM. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008; 51:1403-1419 - PubMed
-
- Pierdomenico SD, Lapenna D, Bucci A, Di Tommaso R, Di Mascio R, Manente BM, Caldarella MP, Neri M, Cuccurullo F, Mezzetti A. Cardiovascular outcome in treated hypertensive patients with responder, masked, false resistant, and true resistant hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2005; 18:1422-1428 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01-RR00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG032631/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-68164/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL649141/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-68162/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL649241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-68163/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U0164829/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 HL064829/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL69751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R03AG032631/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-68161/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical