Transverse coronoid fracture: when does it have to be fixed?
- PMID: 24585321
- PMCID: PMC4048411
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-014-3477-1
Transverse coronoid fracture: when does it have to be fixed?
Abstract
Background: After elbow fracture-dislocation, surgeons confront numerous treatment options in pursuing a stable joint for early motion. The relative contributions of the radial head and coronoid, in combination, to elbow stability have not been defined fully.
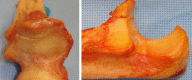
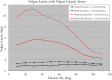
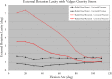
Questions/purposes: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of an approximately 50% transverse coronoid fracture and fixation in the setting of an intact or resected radial head on coronal (varus/valgus) and axial (internal and external rotational) laxity in (1) gravity varus stress; and (2) gravity valgus stress models.
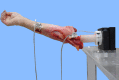
Methods: Kinematic data were collected on six fresh-frozen cadaveric upper extremities tested with passive motion throughout the flexion arc under varus and valgus gravity stress with lateral collateral ligaments reconstructed. Testing included coronoid fracture and osteosynthesis with and without a radial head.
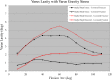
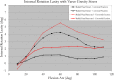
Results: In the varus gravity stress model, fixation of the coronoid improved varus stability (fixed: 1.6° [95% confidence interval, 1.0-2.2], fractured: 5.6° [4.2-7.0], p < 0.001) and internal rotational stability (fixed: 1.8° [0.9-2.7], fractured: 5.4° [4.0-6.8], p < 0.001), but radial head fixation did not contribute to varus stability (intact head: 2.7° [1.3-4.1], resected head: 3.8° [2.3-5.3], p = 0.4) or rotational stability (intact: 2.7° [0.9-4.5], resected head: 3.9° [1.5-6.3], p = 0.4). With valgus stress, coronoid fixation improved valgus stability (fixed: 2.1° [1.0-3.1], fractured: 3.8° [1.8-5.8], p < 0.04) and external rotation stability (fixed: 0.8° [0.1-1.5], fractured: 2.1° [0.9-3.4], p < 0.04), but the radial head played a more important role in providing valgus stability (intact: 1.4° [0.8-2.0], resected head: 7.1° [3.5-10.7], p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Fixation of a 50% transverse coronoid fracture improves varus and internal rotatory laxity but is unlikely to meaningfully improve valgus or external rotation laxity. The radial head, on the other hand, is a stabilizer to resist valgus stress regardless of the status of the coronoid.
Clinical relevance: Determination as to whether it is necessary to fix a coronoid fracture should be based on the stability of the elbow when tested with a varus load. The elbow may potentially be stable with fractures involving less than 50% of the coronoid. Under all circumstances, the radial head should be fixed or replaced to ensure valgus external rotatory stability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radial head reconstruction in elbow fracture-dislocation: monopolar or bipolar prosthesis?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jul;472(7):2144-50. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3672-0. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24867446 Free PMC article.
-
Terrible triad injuries of the elbow: does the coronoid always need to be fixed?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jul;472(7):2084-91. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3471-7. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24474322 Free PMC article.
-
Fixation versus replacement of radial head in terrible triad: is there a difference in elbow stability and prognosis?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jul;472(7):2128-35. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3331-x. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24136807 Free PMC article.
-
Standard surgical protocol to treat elbow dislocations with radial head and coronoid fractures. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005 Mar;87 Suppl 1(Pt 1):22-32. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.D.02933. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. PMID: 15743844 Review.
-
Complex Elbow Instability: Radial Head and Coronoid.Hand Clin. 2015 Nov;31(4):547-56. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Hand Clin. 2015. PMID: 26498544 Review.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of coronoid-first repair through an anterior approach in patients with terrible triad injury of the elbow: a prospective study with a minimum 2-year follow-up.J Orthop Traumatol. 2024 Nov 21;25(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s10195-024-00804-z. J Orthop Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 39570520 Free PMC article.
-
[Monteggia-like injuries : Pitfalls of surgical treatment].Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2023 Sep;126(9):687-693. doi: 10.1007/s00113-023-01328-7. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37278731 Review. German.
-
Coronoid fractures and traumatic elbow instability.JSES Int. 2023 Apr 20;7(6):2587-2593. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2023.03.020. eCollection 2023 Nov. JSES Int. 2023. PMID: 37969528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terrible triad injury of the elbow: a spectrum of theories.JSES Int. 2023 Apr 15;7(6):2565-2568. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2023.03.018. eCollection 2023 Nov. JSES Int. 2023. PMID: 37969512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction of the coronoid process with the olecranon tip for chronic elbow dislocation in children: A rare case report and literature review.Front Pediatr. 2022 Nov 24;10:977866. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.977866. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36507138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beingessner DM, Stacpoole RA, Dunning CE, Johnson JA, King GJ. The effect of suture fixation of type I coronoid fractures on the kinematics and stability of the elbow with and without medial collateral ligament repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:213–217. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2006.06.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Closkey RF, Goode JR, Kirschenbaum D, Cody RP. The role of the coronoid process in elbow stability. A biomechanical analysis of axial loading. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:1749–1753. - PubMed
-
- Morrey BF. Complex instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79:460–469.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

