Natural polymorphisms in Tap2 influence negative selection and CD4∶CD8 lineage commitment in the rat
- PMID: 24586191
- PMCID: PMC3930506
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004151
Natural polymorphisms in Tap2 influence negative selection and CD4∶CD8 lineage commitment in the rat
Abstract
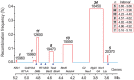
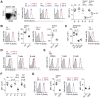
Genetic variation in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) affects CD4∶CD8 lineage commitment and MHC expression. However, the contribution of specific genes in this gene-dense region has not yet been resolved. Nor has it been established whether the same genes regulate MHC expression and T cell selection. Here, we assessed the impact of natural genetic variation on MHC expression and CD4∶CD8 lineage commitment using two genetic models in the rat. First, we mapped Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) associated with variation in MHC class I and II protein expression and the CD4∶CD8 T cell ratio in outbred Heterogeneous Stock rats. We identified 10 QTLs across the genome and found that QTLs for the individual traits colocalized within a region spanning the MHC. To identify the genes underlying these overlapping QTLs, we generated a large panel of MHC-recombinant congenic strains, and refined the QTLs to two adjacent intervals of ∼0.25 Mb in the MHC-I and II regions, respectively. An interaction between these intervals affected MHC class I expression as well as negative selection and lineage commitment of CD8 single-positive (SP) thymocytes. We mapped this effect to the transporter associated with antigen processing 2 (Tap2) in the MHC-II region and the classical MHC class I gene(s) (RT1-A) in the MHC-I region. This interaction was revealed by a recombination between RT1-A and Tap2, which occurred in 0.2% of the rats. Variants of Tap2 have previously been shown to influence the antigenicity of MHC class I molecules by altering the MHC class I ligandome. Our results show that a restricted peptide repertoire on MHC class I molecules leads to reduced negative selection of CD8SP cells. To our knowledge, this is the first study showing how a recombination between natural alleles of genes in the MHC influences lineage commitment of T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Flajnik MF, Kasahara M (2001) Comparative genomics of the MHC: glimpses into the evolution of the adaptive immune system. Immunity 15: 351–362. - PubMed
-
- Complete sequence and gene map of a human major histocompatibility complex. The MHC sequencing (1999) Complete sequence and gene map of a human major histocompatibility complex. The MHC sequencing consortium. Nature 401: 921–923 doi:10.1038/44853 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Trowsdale J, Knight JC (2013) Major histocompatibility complex genomics and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 14: 301–323 doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153455 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fernando MMA, Stevens CR, Walsh EC, De Jager PL, Goyette P, et al. (2008) Defining the role of the MHC in autoimmunity: a review and pooled analysis. PLoS Genet 4: e1000024 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, et al. (2002) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296: 2225–2229 doi:10.1126/science.1069424 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

