Chromosome I controls chromosome II replication in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 24586205
- PMCID: PMC3937223
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004184
Chromosome I controls chromosome II replication in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
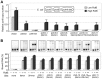
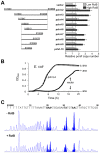
Control of chromosome replication involves a common set of regulators in eukaryotes, whereas bacteria with divided genomes use chromosome-specific regulators. How bacterial chromosomes might communicate for replication is not known. In Vibrio cholerae, which has two chromosomes (chrI and chrII), replication initiation is controlled by DnaA in chrI and by RctB in chrII. DnaA has binding sites at the chrI origin of replication as well as outside the origin. RctB likewise binds at the chrII origin and, as shown here, to external sites. The binding to the external sites in chrII inhibits chrII replication. A new kind of site was found in chrI that enhances chrII replication. Consistent with its enhancing activity, the chrI site increased RctB binding to those chrII origin sites that stimulate replication and decreased binding to other sites that inhibit replication. The differential effect on binding suggests that the new site remodels RctB. The chaperone-like activity of the site is supported by the finding that it could relieve the dependence of chrII replication on chaperone proteins DnaJ and DnaK. The presence of a site in chrI that specifically controls chrII replication suggests a mechanism for communication between the two chromosomes for replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
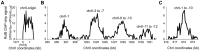


References
-
- Harrison PW, Lower RP, Kim NK, Young JP (2010) Introducing the bacterial ‘chromid’: not a chromosome, not a plasmid. Trends Microbiol 18: 141–148. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami H, Katayama T (2010) DnaA, ORC, and Cdc6: similarity beyond the domains of life and diversity. Biochem Cell Biol 88: 49–62. - PubMed
-
- Giraldo R (2003) Common domains in the initiators of DNA replication in Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya: combined structural, functional and phylogenetic perspectives. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26: 533–554. - PubMed
-
- Egan ES, Fogel MA, Waldor MK (2005) Divided genomes: negotiating the cell cycle in prokaryotes with multiple chromosomes. Mol Microbiol 56: 1129–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

