Quantitative trait loci affecting atherosclerosis at the aortic root identified in an intercross between DBA2J and 129S6 apolipoprotein E-null mice
- PMID: 24586312
- PMCID: PMC3930552
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088274
Quantitative trait loci affecting atherosclerosis at the aortic root identified in an intercross between DBA2J and 129S6 apolipoprotein E-null mice
Abstract
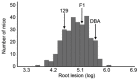
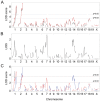
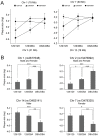
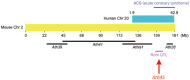
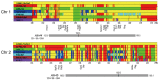
Apolipoprotein E-null mice on a DBA/2J genetic background (DBA-apoE) are highly susceptible to atherosclerosis in the aortic root area compared with those on a 129S6 background (129-apoE). To explore atherosclerosis-responsible genetic regions, we performed a quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis using 172 male and 137 female F2 derived from an intercross between DBA-apoE and 129-apoE mice. A genome-wide scan identified two significant QTL for the size of lesions at the root: one is Ath44 on Chromosome (Chr) 1 at 158 Mb, and the other Ath45 on Chr 2 at 162 Mb. Ath44 co-localizes with but appears to be independent of a previously reported QTL, Ath1, while Ath45 is a novel QTL. DBA alleles of both Ath44 and Ath45 confer atherosclerosis-susceptibility. In addition, a QTL on Chr 14 at 73 Mb was found significant only in males, and 129 allele conferring susceptibility. Further analysis detected female-specific interactions between a second QTL on Chr 1 at 73 Mb and a QTL on Chr 3 at 21 Mb, and between Chr 7 at 84 Mb and Chr 12 at 77 Mb. These loci for the root atherosclerosis were independent of QTLs for plasma total cholesterol and QTLs for triglycerides, but a QTL for HDL (Chr 1 at 126 Mb) overlapped with the Ath44. Notably, haplotype analysis among 129S6, DBA/2J and C57BL/6 genomes and their gene expression data narrowed the candidate regions for Ath44 and Ath45 to less than 5 Mb intervals where multiple genome wide associations with cardiovascular phenotypes have also been reported in humans. SNPs in or near Fmo3, Sele and Selp for Ath44, and Lbp and Pkig for Ath45 were suggested for further investigation as potential candidates underlying the atherosclerosis susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Prins BP, Lagou V, Asselbergs FW, Snieder H, Fu J (2012) Genetics of coronary artery disease: Genome-wide association studies and beyond. Atherosclerosis 225: 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Smith JD, James D, Dansky HM, Wittkowski KM, Moore KJ, et al. (2003) In silico quantitative trait locus map for atherosclerosis susceptibility in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23: 117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

