Treadmill workstations: the effects of walking while working on physical activity and work performance
- PMID: 24586359
- PMCID: PMC3930588
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088620
Treadmill workstations: the effects of walking while working on physical activity and work performance
Abstract
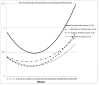
We conducted a 12-month-long experiment in a financial services company to study how the availability of treadmill workstations affects employees' physical activity and work performance. We enlisted sedentary volunteers, half of whom received treadmill workstations during the first two months of the study and the rest in the seventh month of the study. Participants could operate the treadmills at speeds of 0-2 mph and could use a standard chair-desk arrangement at will. (a) Weekly online performance surveys were administered to participants and their supervisors, as well as to all other sedentary employees and their supervisors. Using within-person statistical analyses, we find that overall work performance, quality and quantity of performance, and interactions with coworkers improved as a result of adoption of treadmill workstations. (b) Participants were outfitted with accelerometers at the start of the study. We find that daily total physical activity increased as a result of the adoption of treadmill workstations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- WHO (World Health Organization) (2002) The World Health Report 2002: Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Available: http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/whr02_en.pdf.
-
- Mummery WK, Schofield GM, Steele R, Eakin EG, Brown WJ (2005) Occupational sitting time and overweight and obesity in Australian workers. American J of Preventive Medicine 29(2): 91–97. - PubMed
-
- Brownell KD (1995) Exercise in the treatment of obesity: Eating disorders and obesity: A Comprehensive Handbook. New York: Guilford Press. 473–478.
-
- Hughes MC, Girolami TM, Cheadle AD, Harris JR, Patrick DL (2007) A lifestyle-based weight management program delivered to employees: Examination of health and economic outcomes. J of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 49(11): 1212–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical