Ischaemic strokes in patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: associations with iron deficiency and platelets
- PMID: 24586400
- PMCID: PMC3929507
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088812
Ischaemic strokes in patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: associations with iron deficiency and platelets
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary first pass filtration of particles marginally exceeding ∼7 µm (the size of a red blood cell) is used routinely in diagnostics, and allows cellular aggregates forming or entering the circulation in the preceding cardiac cycle to lodge safely in pulmonary capillaries/arterioles. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations compromise capillary bed filtration, and are commonly associated with ischaemic stroke. Cohorts with CT-scan evident malformations associated with the highest contrast echocardiographic shunt grades are known to be at higher stroke risk. Our goal was to identify within this broad grouping, which patients were at higher risk of stroke.
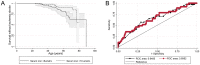
Methodology: 497 consecutive patients with CT-proven pulmonary arteriovenous malformations due to hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia were studied. Relationships with radiologically-confirmed clinical ischaemic stroke were examined using logistic regression, receiver operating characteristic analyses, and platelet studies.
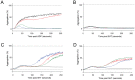
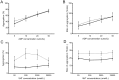
Principal findings: Sixty-one individuals (12.3%) had acute, non-iatrogenic ischaemic clinical strokes at a median age of 52 (IQR 41-63) years. In crude and age-adjusted logistic regression, stroke risk was associated not with venous thromboemboli or conventional neurovascular risk factors, but with low serum iron (adjusted odds ratio 0.96 [95% confidence intervals 0.92, 1.00]), and more weakly with low oxygen saturations reflecting a larger right-to-left shunt (adjusted OR 0.96 [0.92, 1.01]). For the same pulmonary arteriovenous malformations, the stroke risk would approximately double with serum iron 6 µmol/L compared to mid-normal range (7-27 µmol/L). Platelet studies confirmed overlooked data that iron deficiency is associated with exuberant platelet aggregation to serotonin (5HT), correcting following iron treatment. By MANOVA, adjusting for participant and 5HT, iron or ferritin explained 14% of the variance in log-transformed aggregation-rate (p = 0.039/p = 0.021).
Significance: These data suggest that patients with compromised pulmonary capillary filtration due to pulmonary arteriovenous malformations are at increased risk of ischaemic stroke if they are iron deficient, and that mechanisms are likely to include enhanced aggregation of circulating platelets.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Shovlin CL, Jackson JE (2010) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations and other vascular abnormalities. In: Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Martin T, et al. editors. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine.5th Edn. Philadelphia, Elsevier-Saunders. pp. 1261–1282.
-
- Butler BD, Hills BA (1979) The lung as a filter for microbubbles. J Appl Physiol. 1979 47: 537–43. - PubMed
-
- Weibel ER (2009) What makes a good lung? The morphometric basis of lung function. Swiss Med Wkly 139 (27–28): 375–386. - PubMed
-
- Chilvers ER, Peters AM, George P, Hughes JMB, Allison DJ (1989) Quantification of right to left shunt through pulmonary arteriovenous malformations using 99Tcm albumin microspheres. Clin Radiol 39: 611–614. - PubMed
-
- Bajc M, Neilly JB, Miniati M, Schuemichen C, Meignan M, et al. (2009) EANM guidelines for ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy: Part 1. Pulmonary imaging with ventilation/perfusion single photon emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36: 1356–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

