Imaging dynamic molecular signaling by the Cdc42 GTPase within the developing CNS
- PMID: 24586421
- PMCID: PMC3929599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088870
Imaging dynamic molecular signaling by the Cdc42 GTPase within the developing CNS
Abstract
Protein interactions underlie the complexity of neuronal function. Potential interactions between specific proteins in the brain are predicted from assays based on genetic interaction and/or biochemistry. Genetic interaction reveals endogenous, but not necessarily direct, interactions between the proteins. Biochemistry-based assays, on the other hand, demonstrate direct interactions between proteins, but often outside their native environment or without a subcellular context. We aimed to achieve the best of both approaches by visualizing protein interaction directly within the brain of a live animal. Here, we show a proof-of-principle experiment in which the Cdc42 GTPase associates with its alleged partner WASp within neurons during the time and space that coincide with the newly developing CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


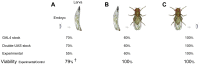



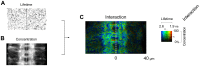

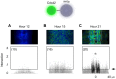


References
-
- Wennerberg K, Rossman KL, Der CJ (2005) The Ras superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci 118: 843–846. - PubMed
-
- Sanes JR, Lichtman JW (1999) Can molecules explain long-term potentiation? Nat Neurosci 2: 597–604. - PubMed
-
- Förster T (1948) Intermolecular energy migration and fluorescence. Annalen der Physik 437: 55–75.
-
- Duffy JB (2002) GAL4 system in Drosophila: a fly geneticist’s Swiss army knife. Genesis 34: 1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

