Node interference and robustness: performing virtual knock-out experiments on biological networks: the case of leukocyte integrin activation network
- PMID: 24586448
- PMCID: PMC3930642
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088938
Node interference and robustness: performing virtual knock-out experiments on biological networks: the case of leukocyte integrin activation network
Abstract
The increasing availability of large network datasets derived from high-throughput experiments requires the development of tools to extract relevant information from biological networks, and the development of computational methods capable of detecting qualitative and quantitative changes in the topological properties of biological networks is of critical relevance. We introduce the notions of node interference and robustness as measures of the reciprocal influence between nodes within a network. We examine the theoretical significance of these new, centrality-based, measures by characterizing the topological relationships between nodes and groups of nodes. Node interference analysis allows topologically determining the context of functional influence of single nodes. Conversely, the node robustness analysis allows topologically identifying the nodes having the highest functional influence on a specific node. A new Cytoscape plug-in calculating these measures was developed and applied to a protein-protein interaction network specifically regulating integrin activation in human primary leukocytes. Notably, the functional effects of compounds inhibiting important protein kinases, such as SRC, HCK, FGR and JAK2, are predicted by the interference and robustness analysis, are in agreement with previous studies and are confirmed by laboratory experiments. The interference and robustness notions can be applied to a variety of different contexts, including, for instance, the identification of potential side effects of drugs or the characterization of the consequences of genes deletion, duplication or of proteins degradation, opening new perspectives in biological network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




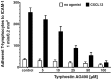
 CXCL12 for 1 min. Plots are averaged values of adherent
CXCL12 for 1 min. Plots are averaged values of adherent  with standard deviation N = 5.
with standard deviation N = 5.Similar articles
-
Analyzing biological network parameters with CentiScaPe.Bioinformatics. 2009 Nov 1;25(21):2857-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp517. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19729372 Free PMC article.
-
CytoNCA: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks.Biosystems. 2015 Jan;127:67-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Biosystems. 2015. PMID: 25451770
-
Virtual pathway explorer (viPEr) and pathway enrichment analysis tool (PEANuT): creating and analyzing focus networks to identify cross-talk between molecules and pathways.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 14;16:790. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2017-z. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26467653 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin signal transduction in myeloid leukocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Mar;65(3):313-20. doi: 10.1002/jlb.65.3.313. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10080533 Review.
-
Computational methods for identifying the critical nodes in biological networks.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Mar 23;21(2):486-497. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz011. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30753282 Review.
Cited by
-
Game theoretic centrality: a novel approach to prioritize disease candidate genes by combining biological networks with the Shapley value.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Aug 12;21(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03693-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32787845 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced G protein signaling despite impaired internalization and β-arrestin recruitment in patients carrying a CXCR4Leu317fsX3 mutation causing WHIM syndrome.JCI Insight. 2023 Mar 8;8(5):e145688. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.145688. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 36883568 Free PMC article.
-
Topological alternate centrality measure capturing drug targets in the network of MAPK pathways.IET Syst Biol. 2018 Oct;12(5):226-232. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2017.0058. IET Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 30259868 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic landscape of rheumatoid arthritis: re-evaluation of drug adverse effects.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Nov 4;2:59. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00059. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25414848 Free PMC article.
-
Breeding custom-designed crops for improved drought adaptation.Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2021 Sep 20;2(3):e202100017. doi: 10.1002/ggn2.202100017. eCollection 2021 Sep. Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 36620433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caldarelli G (2007) Scale-Free Networks: Complex Webs in Nature and Technology (Oxford Finance). Oxford University Press, USA. Available: http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/redirect?tag=citeulike07-20&path=ASIN/....
-
- Bhalla US, Iyengar R (1999) Emergent properties of networks of biological signaling pathways. Science 283. - PubMed
-
- Strogatz SH (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature 410: 268–276. - PubMed
-
- Barabási AL, Albert R (1999) Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286: 509–512. - PubMed
-
- Jeong H, Tombor B, Albert R, Oltvai ZN, Barabási AL (2000) The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 407: 651–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

