An in vitro study on the effects of nisin on the antibacterial activities of 18 antibiotics against Enterococcus faecalis
- PMID: 24586598
- PMCID: PMC3930635
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089209
An in vitro study on the effects of nisin on the antibacterial activities of 18 antibiotics against Enterococcus faecalis
Abstract
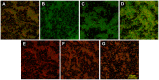
Enterococcus faecalis rank among the leading causes of nosocomial infections worldwide and possesses both intrinsic and acquired resistance to a variety of antibiotics. Development of new antibiotics is limited, and pathogens continually generate new antibiotic resistance. Many researchers aim to identify strategies to effectively kill this drug-resistant pathogen. Here, we evaluated the effect of the antimicrobial peptide nisin on the antibacterial activities of 18 antibiotics against E. faecalis. The MIC and MBC results showed that the antibacterial activities of 18 antibiotics against E. faecalis OG1RF, ATCC 29212, and strain E were significantly improved in the presence of 200 U/ml nisin. Statistically significant differences were observed between the results with and without 200 U/ml nisin at the same concentrations of penicillin or chloramphenicol (p<0.05). The checkerboard assay showed that the combination of nisin and penicillin or chloramphenicol had a synergetic effect against the three tested E. faecalis strains. The transmission electron microscope images showed that E. faecalis was not obviously destroyed by penicillin or chloramphenicol alone but was severely disrupted by either antibiotic in combination with nisin. Furthermore, assessing biofilms by a confocal laser scanning microscope showed that penicillin, ciprofloxacin, and chloramphenicol all showed stronger antibiofilm actions in combination with nisin than when these antibiotics were administered alone. Therefore, nisin can significantly improve the antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of many antibiotics, and certain antibiotics in combination with nisin have considerable potential for use as inhibitors of this drug-resistant pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of MTADN on 10 Enterococcus faecalis isolates and biofilm: an in vitro study.J Endod. 2013 May;39(5):674-8. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.12.010. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Endod. 2013. PMID: 23611389
-
In vitro evaluation of the antibacterial activities of MTAD in combination with nisin against Enterococcus faecalis.J Endod. 2011 Aug;37(8):1116-20. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.03.020. Epub 2011 May 8. J Endod. 2011. PMID: 21763904
-
Effects of intracanal irrigant MTAD Combined with nisin at sub-minimum inhibitory concentration levels on Enterococcus faecalis growth and the expression of pathogenic genes.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 6;9(3):e90235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090235. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24603760 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcal Infections: New Compounds, Novel Antimicrobial Therapies?Trends Microbiol. 2017 Jun;25(6):467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Trends Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28209400 Review.
-
Antibiofilm activity of phytochemicals against Enterococcus faecalis: A literature review.Phytother Res. 2022 Jul;36(7):2824-2838. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7488. Epub 2022 May 6. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 35522168 Review.
Cited by
-
Oligopolyphenylenevinylene-conjugated oligoelectrolyte membrane insertion molecules selectively disrupt cell envelopes of Gram-positive bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Mar;81(6):1949-58. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03355-14. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25576607 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro synergistic activities of cefazolin and nisin A against mastitis pathogens.J Vet Med Sci. 2017 Sep 12;79(9):1472-1479. doi: 10.1292/jvms.17-0180. Epub 2017 Jul 29. J Vet Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28757508 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Activities of Nisin and Nisin Derivatives Alone and In Combination with Antibiotics against Staphylococcus Biofilms.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 18;7:508. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00508. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27148197 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of nisin and p-coumaric acid on autoinducer-2 activity, biofilm formation, and sprE expression of Enterococcus faecalis.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Jun;54(2):601-608. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-00946-y. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36930448 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Characterization of a Novel Cold Shock Protein-Like Bacteriocin Synthesized by Bacillus thuringiensis.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 20;6:35560. doi: 10.1038/srep35560. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27762322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hadley EB, Hancock RE (2010) Strategies for the discovery and advancement of novel cationic antimicrobial peptides. Curr Top Med Chem 10: 1872–1881. - PubMed
-
- Severina E, Severin A, Tomasz A (1998) Antibacterial efficacy of nisin against multidrug-resistant Gram-positive pathogens. J Antimicrob Chemother 41: 341–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

