Nuclear receptor 4a3 (nr4a3) regulates murine mast cell responses and granule content
- PMID: 24586680
- PMCID: PMC3930735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089311
Nuclear receptor 4a3 (nr4a3) regulates murine mast cell responses and granule content
Abstract
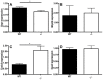
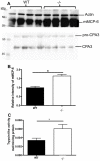
Nuclear receptor 4a3 (Nr4a3) is a transcription factor implicated in various settings such as vascular biology and inflammation. We have recently shown that mast cells dramatically upregulate Nuclear receptor 4a3 upon activation, and here we investigated the functional impact of Nuclear receptor 4a3 on mast cell responses. We show that Nuclear receptor 4a3 is involved in the regulation of cytokine/chemokine secretion in mast cells following activation via the high affinity IgE receptor. Moreover, Nuclear receptor 4a3 negatively affects the transcript and protein levels of mast cell tryptase as well as the mast cell's responsiveness to allergen. Together, these findings identify Nuclear receptor 4a3 as a novel regulator of mast cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Metcalfe DD, Baram D, Mekori YA (1997) Mast cells. Physiol Rev 77: 1033–1079. - PubMed
-
- Pejler G, Rönnberg E, Waern I, Wernersson S (2010) Mast cell proteases: multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease. Blood 115: 4981–4990. - PubMed
-
- Murakami M, Iwata Y, Funaba M (2007) Expression and transcriptional activity of alternative splice variants of Mitf exon 6. Mol Cell Biochem 303: 251–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

