Multiple sleep alterations in mice lacking cannabinoid type 1 receptors
- PMID: 24586776
- PMCID: PMC3930731
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089432
Multiple sleep alterations in mice lacking cannabinoid type 1 receptors
Abstract
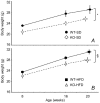
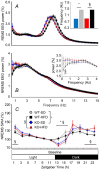
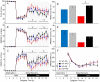
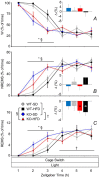
Cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors are highly expressed in the brain and play a role in behavior control. Endogenous cannabinoid signaling is modulated by high-fat diet (HFD). We investigated the consequences of congenital lack of CB1 receptors on sleep in mice fed standard diet (SD) and HFD. CB1 cannabinoid receptor knock-out (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice were fed SD or HFD for 4 months (n = 9-10 per group). Mice were instrumented with electroencephalographic (EEG) and electromyographic electrodes. Recordings were performed during baseline (48 hours), sleep deprivation (gentle handling, 6 hours), sleep recovery (18 hours), and after cage switch (insomnia model paradigm, 6 hours). We found multiple significant effects of genotype on sleep. In particular, KO spent more time awake and less time in non-rapid-eye-movement sleep (NREMS) and rapid-eye-movement sleep (REMS) than WT during the dark (active) period but not during the light (rest) period, enhancing the day-night variation of wake-sleep amounts. KO had slower EEG theta rhythm during REMS. REMS homeostasis after sleep deprivation was less effective in KO than in WT. Finally, KO habituated more rapidly to the arousing effect of the cage-switch test than WT. We did not find any significant effects of diet or of diet x genotype interaction on sleep. The occurrence of multiple sleep alterations in KO indicates important roles of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in limiting arousal during the active period of the day, in sleep regulation, and in sleep EEG in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI (1990) Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 346: 561–564. - PubMed
-
- Huestis MA, Gorelick DA, Heishman SJ, Preston KL, Nelson RA, et al. (2001) Blockade of effects of smoked marijuana by the CB1-selective cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58: 322–328. - PubMed
-
- Di Marzo V, Melck D, Bisogno T, De Petrocellis L (1998) Endocannabinoids: endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligands with neuromodulatory action. Trends Neurosci 21: 521–528. - PubMed
-
- Mechoulam R, Parker LA (2013) The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annu Rev Psychol 64: 21–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

