RNA CoMPASS: a dual approach for pathogen and host transcriptome analysis of RNA-seq datasets
- PMID: 24586784
- PMCID: PMC3934900
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089445
RNA CoMPASS: a dual approach for pathogen and host transcriptome analysis of RNA-seq datasets
Abstract
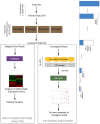
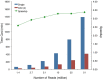
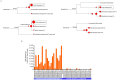
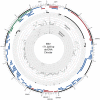
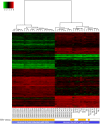
High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) has become an instrumental assay for the analysis of multiple aspects of an organism's transcriptome. Further, the analysis of a biological specimen's associated microbiome can also be performed using RNA-seq data and this application is gaining interest in the scientific community. There are many existing bioinformatics tools designed for analysis and visualization of transcriptome data. Despite the availability of an array of next generation sequencing (NGS) analysis tools, the analysis of RNA-seq data sets poses a challenge for many biomedical researchers who are not familiar with command-line tools. Here we present RNA CoMPASS, a comprehensive RNA-seq analysis pipeline for the simultaneous analysis of transcriptomes and metatranscriptomes from diverse biological specimens. RNA CoMPASS leverages existing tools and parallel computing technology to facilitate the analysis of even very large datasets. RNA CoMPASS has a web-based graphical user interface with intrinsic queuing to control a distributed computational pipeline. RNA CoMPASS was evaluated by analyzing RNA-seq data sets from 45 B-cell samples. Twenty-two of these samples were derived from lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) generated by the infection of naïve B-cells with the Epstein Barr virus (EBV), while another 23 samples were derived from Burkitt's lymphomas (BL), some of which arose in part through infection with EBV. Appropriately, RNA CoMPASS identified EBV in all LCLs and in a fraction of the BLs. Cluster analysis of the human transcriptome component of the RNA CoMPASS output clearly separated the BLs (which have a germinal center-like phenotype) from the LCLs (which have a blast-like phenotype) with evidence of activated MYC signaling and lower interferon and NF-kB signaling in the BLs. Together, this analysis illustrates the utility of RNA CoMPASS in the simultaneous analysis of transcriptome and metatranscriptome data. RNA CoMPASS is freely available at http://rnacompass.sourceforge.net/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
SPARTA: Simple Program for Automated reference-based bacterial RNA-seq Transcriptome Analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Feb 4;17:66. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-0923-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26847232 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico HLA Typing Using Standard RNA-Seq Sequence Reads.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1310:247-58. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2690-9_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26024640
-
UTAP: User-friendly Transcriptome Analysis Pipeline.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Mar 25;20(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2728-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30909881 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression Analysis of RNA-seq Reads: Overview, Taxonomy, and Tools.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2020 Mar-Apr;17(2):566-586. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2018.2873010. Epub 2018 Oct 1. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30281477 Review.
-
Elucidating the editome: bioinformatics approaches for RNA editing detection.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Mar 22;20(2):436-447. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx129. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29040360 Review.
Cited by
-
From command-line bioinformatics to bioGUI.PeerJ. 2019 Nov 21;7:e8111. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8111. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31772845 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 31;11(6):759. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060759. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31159203 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the conversation on high-throughput virome sequencing standards to include consideration of microbial contamination sources.mBio. 2014 Oct 28;5(6):e01989. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01989-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25352620 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advanced Applications of RNA Sequencing and Challenges.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2015 Nov 15;9(Suppl 1):29-46. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S28991. eCollection 2015. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2015. PMID: 26609224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legume-rhizobia symbiosis: Translatome analysis.Genet Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 1;47Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e20230284. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2023-0284. eCollection 2024. Genet Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38954532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coco JR, EK Flemington, CM Taylor (2011) PARSES: A Pipeline for Analysis of RNA-Seq Exogenous Sequences. Proceedings of the ISCA 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. Holiday Inn Downtown-Superdome, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA 2011: BICoB-2011. pp. 196–200.
-
- Weber G, Shendure J, Tanenbaum DM, Church GM, Meyerson M (2002) Identification of foreign gene sequences by transcript filtering against the human genome. Nat Genet 30: 141–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

