Ectopic expression of GsPPCK3 and SCMRP in Medicago sativa enhances plant alkaline stress tolerance and methionine content
- PMID: 24586886
- PMCID: PMC3934933
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089578
Ectopic expression of GsPPCK3 and SCMRP in Medicago sativa enhances plant alkaline stress tolerance and methionine content
Abstract
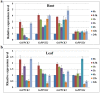
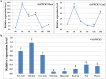
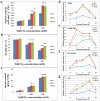
So far, it has been suggested that phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylases (PEPCs) and PEPC kinases (PPCKs) fulfill several important non-photosynthetic functions. However, the biological functions of soybean PPCKs, especially in alkali stress response, are not yet well known. In previous studies, we constructed a Glycine soja transcriptional profile, and identified three PPCK genes (GsPPCK1, GsPPCK2 and GsPPCK3) as potential alkali stress responsive genes. In this study, we confirmed the induced expression of GsPPCK3 under alkali stress and investigated its tissue expression specificity by using quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Then we ectopically expressed GsPPCK3 in Medicago sativa and found that GsPPCK3 overexpression improved plant alkali tolerance, as evidenced by lower levels of relative ion leakage and MDA content and higher levels of chlorophyll content and root activity. In this respect, we further co-transformed the GsPPCK3 and SCMRP genes into alfalfa, and demonstrated the increased alkali tolerance of GsPPCK3-SCMRP transgenic lines. Further investigation revealed that GsPPCK3-SCMRP co-overexpression promoted the PEPC activity, net photosynthetic rate and citric acid content of transgenic alfalfa under alkali stress. Moreover, we also observed the up-regulated expression of PEPC, CS (citrate synthase), H(+)-ATPase and NADP-ME genes in GsPPCK3-SCMRP transgenic alfalfa under alkali stress. As expected, we demonstrated that GsPPCK3-SCMRP transgenic lines displayed higher methionine content than wild type alfalfa. Taken together, results presented in this study supported the positive role of GsPPCK3 in plant response to alkali stress, and provided an effective way to simultaneously improve plant alkaline tolerance and methionine content, at least in legume crops.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase kinase gene MsPPCK1 from Medicago sativa L. increased alkali tolerance of alfalfa by enhancing photosynthetic efficiency and promoting nodule development.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Aug;213:108764. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108764. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38879983
-
Overexpression of GsGSTU13 and SCMRP in Medicago sativa confers increased salt-alkaline tolerance and methionine content.Physiol Plant. 2016 Feb;156(2):176-189. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12350. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Physiol Plant. 2016. PMID: 26010993
-
Overexpression of GsZFP1 enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013 Oct;71:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23867600
-
Alfalfa MsCBL4 enhances calcium metabolism but not sodium transport in transgenic tobacco under salt and saline-alkali stress.Plant Cell Rep. 2020 Aug;39(8):997-1011. doi: 10.1007/s00299-020-02543-x. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Plant Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32333150
-
The Impact of Alkaline Stress on Plant Growth and Its Alkaline Resistance Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 23;25(24):13719. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413719. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel Glycine soja homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) I gene, Gshdz4, positively regulates bicarbonate tolerance and responds to osmotic stress in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Aug 24;16(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0872-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27553065 Free PMC article.
-
A Glycine soja group S2 bZIP transcription factor GsbZIP67 conferred bicarbonate alkaline tolerance in Medicago sativa.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 13;18(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1466-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30316294 Free PMC article.
-
Response Mechanisms of Plants Under Saline-Alkali Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 4;12:667458. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.667458. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34149764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of MsRCI2A, MsRCI2B, and MsRCI2C in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Provides Different Extents of Enhanced Alkali and Salt Tolerance Due to Functional Specialization of MsRCI2s.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Aug 19;12:702195. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.702195. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34490005 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of an alfalfa glutathione S-transferase gene improved the saline-alkali tolerance of transgenic tobacco.Biol Open. 2019 Sep 9;8(9):bio043505. doi: 10.1242/bio.043505. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31471294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Postnikova OA, Shao J, Nemchinov LG (2013) Analysis of the alfalfa root transcriptome in response to salinity stress. Plant Cell Physiol 54: 1041–1055. - PubMed
-
- Jin H, Plaha P, Park JY, Hong CP, Lee IS, et al. (2006) Comparative EST profiles of leaf and root of Leymus chinensis, a xerophilous grass adapted to high pH sodic soil. Plant Sci 170: 1081–1086.
-
- Wang Y, Ma H, Liu G, Xu C, Zhang D, et al. (2008) Analysis of gene expression profile of Limonium bicolor under NaHCO3 stress using cDNA microarray. Plant Mol Biol Rep 26: 241–254.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

