Modulation by K+ Plus NH4+ of microsomal (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in selected ontogenetic stages of the diadromous river shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae)
- PMID: 24586919
- PMCID: PMC3931822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089625
Modulation by K+ Plus NH4+ of microsomal (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in selected ontogenetic stages of the diadromous river shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae)
Abstract
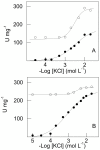
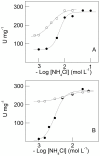
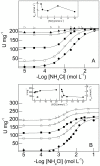
We investigate the synergistic stimulation by K(+) plus NH4 (+) of (Na(+), K(+))-ATPase activity in microsomal preparations of whole zoea I and decapodid III, and in juvenile and adult river shrimp gills. Modulation of (Na(+), K(+))-ATPase activity is ontogenetic stage-specific, and particularly distinct between juveniles and adults. Although both gill enzymes exhibit two different sites for K(+) and NH4 (+) binding, in the juvenile enzyme, these two sites are equivalent: binding by both ions results in slightly stimulated activity compared to that of a single ionic species. In the adult enzyme, the sites are not equivalent: when one ion occupies its specific binding site, (Na(+), K(+))-ATPase activity is stimulated synergistically by ≈ 50% on binding of the complementary ion. Immunolocalization reveals the enzyme to be distributed predominantly throughout the intralamellar septum in the gill lamellae of juveniles and adults. Western blot analyses demonstrate a single immunoreactive band, suggesting a single (Na(+), K(+))-ATPase α-subunit isoform that is distributed into different density membrane fractions, independently of ontogenetic stage. We propose a model for the modulation by K(+) and NH4 (+) of gill (Na(+), K(+))-ATPase activity. These findings suggest that the gill enzyme may be regulated by NH4 (+) during ontogenetic development in M. amazonicum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Jorgensen PL, Hakansson KO, Karlish SJD (2003) Structure and mechanism of Na,K-ATPase: Functional sites and their interactions. Ann Rev Physiol 65: 817–849. - PubMed
-
- Martin DW (2005) Structure-function relationships in the Na+, K+-pump. Semin Nephrol 25: 282–291. - PubMed
-
- Sáez AG, Lozano E, Zaldívar-Riverón A (2009) Evolutionary history of Na,K-ATPases and their osmoregulatory role. Genetica 136: 479–490. - PubMed
-
- Axelsen MG, Palmgren KB (1998) Evolution of P-type ATPases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1365: 37–45. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen PL, Pedersen PA (2001) Structure-function relationships of Na+, K+, ATP, or Mg2+ binding and energy transduction in Na+,K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1505: 57–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

