Remote control of respiratory neural network by spinal locomotor generators
- PMID: 24586951
- PMCID: PMC3930745
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089670
Remote control of respiratory neural network by spinal locomotor generators
Abstract
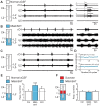
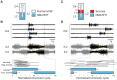
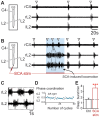
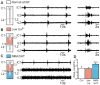
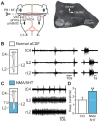
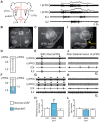
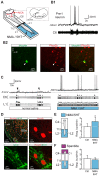
During exercise and locomotion, breathing rate rapidly increases to meet the suddenly enhanced oxygen demand. The extent to which direct central interactions between the spinal networks controlling locomotion and the brainstem networks controlling breathing are involved in this rhythm modulation remains unknown. Here, we show that in isolated neonatal rat brainstem-spinal cord preparations, the increase in respiratory rate observed during fictive locomotion is associated with an increase in the excitability of pre-inspiratory neurons of the parafacial respiratory group (pFRG/Pre-I). In addition, this locomotion-induced respiratory rhythm modulation is prevented both by bilateral lesion of the pFRG region and by blockade of neurokinin 1 receptors in the brainstem. Thus, our results assign pFRG/Pre-I neurons a new role as elements of a previously undescribed pathway involved in the functional interaction between respiratory and locomotor networks, an interaction that also involves a substance P-dependent modulating mechanism requiring the activation of neurokinin 1 receptors. This neurogenic mechanism may take an active part in the increased respiratory rhythmicity produced at the onset and during episodes of locomotion in mammals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anoxic persistence of lumbar respiratory bursts and block of lumbar locomotion in newborn rat brainstem spinal cords.J Physiol. 2007 Dec 1;585(Pt 2):507-24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143594. Epub 2007 Oct 11. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17932145 Free PMC article.
-
Bimodal Respiratory-Locomotor Neurons in the Neonatal Rat Spinal Cord.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 20;36(3):926-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1825-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26791221 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem Steering of Locomotor Activity in the Newborn Rat.J Neurosci. 2018 Aug 29;38(35):7725-7740. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1074-18.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30037828 Free PMC article.
-
The respiratory control mechanisms in the brainstem and spinal cord: integrative views of the neuroanatomy and neurophysiology.J Physiol Sci. 2017 Jan;67(1):45-62. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0475-y. Epub 2016 Aug 17. J Physiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27535569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of the respiratory center using isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparations.Neurosci Res. 1995 Jan;21(3):183-90. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(94)00863-b. Neurosci Res. 1995. PMID: 7753499 Review.
Cited by
-
Breath Tools: A Synthesis of Evidence-Based Breathing Strategies to Enhance Human Running.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 17;13:813243. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.813243. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35370762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of DSCAM in the Development of Neural Control of Movement and Locomotion.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 7;22(16):8511. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168511. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Activity-Based Therapy on Respiratory Outcomes in a Medically Complex Child.Children (Basel). 2021 Jan 9;8(1):36. doi: 10.3390/children8010036. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33435403 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve restores inspiratory diaphragm function in mice after spinal cord injury.Front Neural Circuits. 2025 Jan 22;18:1480291. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2024.1480291. eCollection 2024. Front Neural Circuits. 2025. PMID: 39911754 Free PMC article.
-
Deconstructing the modular organization and real-time dynamics of mammalian spinal locomotor networks.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 16;14(1):873. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36587-w. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36797254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mateika JH, Duffin J (1995) A review of the control of breathing during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 71: 1–27. - PubMed
-
- Haouzi P, Hirsch JJ, Marchal F, Huszczuk A (1997) Ventilatory and gas exchange response during walking in severe peripheral vascular disease. Respir Physiol 107: 181–190. - PubMed
-
- Tobin MJ, Perez W, Guenther SM, D'Alonzo G, Dantzker DR (1986) Breathing pattern and metabolic behavior during anticipation of exercise. J Appl Physiol 60: 1306–1312. - PubMed
-
- Gravel J, Brocard F, Gariepy JF, Lund JP, Dubuc R (2007) Modulation of respiratory activity by locomotion in lampreys. Neuroscience 144: 1120–1132. - PubMed
-
- Bell HJ (2006) Respiratory control at exercise onset: an integrated systems perspective. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 152: 1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

