Molecular cloning of a novel glucuronokinase/putative pyrophosphorylase from zebrafish acting in an UDP-glucuronic acid salvage pathway
- PMID: 24586965
- PMCID: PMC3938481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089690
Molecular cloning of a novel glucuronokinase/putative pyrophosphorylase from zebrafish acting in an UDP-glucuronic acid salvage pathway
Abstract
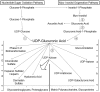
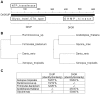
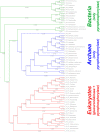
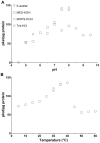
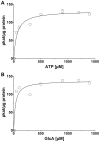
In animals, the main precursor for glycosaminoglycan and furthermore proteoglycan biosynthesis, like hyaluronic acid, is UDP-glucuronic acid, which is synthesized via the nucleotide sugar oxidation pathway. Mutations in this pathway cause severe developmental defects (deficiency in the initiation of heart valve formation). In plants, UDP-glucuronic acid is synthesized via two independent pathways. Beside the nucleotide sugar oxidation pathway, a second minor route to UDP-glucuronic acid exist termed the myo-inositol oxygenation pathway. Within this myo-inositol is ring cleaved into glucuronic acid, which is subsequently converted to UDP-glucuronic acid by glucuronokinase and UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase. Here we report on a similar, but bifunctional enzyme from zebrafish (Danio rerio) which has glucuronokinase/putative pyrophosphorylase activity. The enzyme can convert glucuronic acid into UDP-glucuronic acid, required for completion of the alternative pathway to UDP-glucuronic acid via myo-inositol and thus establishes a so far unknown second route to UDP-glucuronic acid in animals. Glucuronokinase from zebrafish is a member of the GHMP-kinase superfamily having unique substrate specificity for glucuronic acid with a Km of 31 ± 8 µM and accepting ATP as the only phosphate donor (Km: 59 ± 9 µM). UDP-glucuronic acid pyrophosphorylase from zebrafish has homology to bacterial nucleotidyltransferases and requires UTP as nucleosid diphosphate donor. Genes for bifunctional glucuronokinase and putative UDP-glucuronic acid pyrophosphorylase are conserved among some groups of lower animals, including fishes, frogs, tunicates, and polychaeta, but are absent from mammals. The existence of a second pathway for UDP-glucuronic acid biosynthesis in zebrafish likely explains some previous contradictory finding in jekyll/ugdh zebrafish developmental mutants, which showed residual glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans in knockout mutants of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cloning of Glucuronokinase from Arabidopsis thaliana, the last missing enzyme of the myo-inositol oxygenase pathway to nucleotide sugars.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 29;285(5):2902-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.069369. Epub 2009 Dec 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19951951 Free PMC article.
-
Nonradioactive enzyme measurement by high-performance liquid chromatography of partially purified sugar-1-kinase (glucuronokinase) from pollen of Lilium longiflorum.Anal Biochem. 2009 May 15;388(2):254-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.03.002. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Anal Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19272347
-
Reconstruction of de novo pathway for synthesis of UDP-glucuronic acid and UDP-xylose from intrinsic UDP-glucose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEBS J. 2006 Jun;273(12):2645-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05281.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16817893
-
UDP-glucose dehydrogenase: structure and function of a potential drug target.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Oct;38(5):1378-85. doi: 10.1042/BST0381378. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20863317 Review.
-
Integration of Sugar Metabolism and Proteoglycan Synthesis by UDP-glucose Dehydrogenase.J Histochem Cytochem. 2021 Jan;69(1):13-23. doi: 10.1369/0022155420947500. Epub 2020 Aug 4. J Histochem Cytochem. 2021. PMID: 32749901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular cloning of AtRS4, a seed specific multifunctional RFO synthase/galactosylhydrolase in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Sep 29;6:789. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00789. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26483807 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Bifunctional Galactokinase/Uridyltransferase Chimera for Enhanced UDP-d-Xylose Production.JACS Au. 2024 Jun 20;4(7):2557-2563. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00288. eCollection 2024 Jul 22. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 39055162 Free PMC article.
-
Loss-of-function mutations in UDP-Glucose 6-Dehydrogenase cause recessive developmental epileptic encephalopathy.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 30;11(1):595. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14360-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32001716 Free PMC article.
-
The Myo-inositol pathway does not contribute to ascorbic acid synthesis.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2019 Jan;21 Suppl 1(Suppl Suppl 1):95-102. doi: 10.1111/plb.12898. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2019. PMID: 30102814 Free PMC article.
-
GHMP gene family: identification, evolutionary and expression analysis under various exogenous hormones and abiotic stress in tomato.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):850. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06857-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40610883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Velleman SG (2000) The role of the extracellular matrix in skeletal development. Poult Sci 79: 985–989. - PubMed
-
- Kirn-Safran CB, Gomes RR, Brown AJ, Carson DD (2004) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: coordinators of multiple signaling pathways during chondrogenesis. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 72: 69–88. - PubMed
-
- Knudson CB, Knudson W (2001) Cartilage proteoglycans. Semin Cell Dev Biol 12: 69–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

