Plasma D-dimer predicts short-term poor outcome after acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 24587013
- PMCID: PMC3933671
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089756
Plasma D-dimer predicts short-term poor outcome after acute ischemic stroke
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Plasma D-Dimer Predicts Short-Term Poor Outcome after Acute Ischemic Stroke.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 30;17(3):e0266437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266437. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35353871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Haemostatic biomarkers associated with poor outcome in acute ischemic stroke (AIS). The objective of the study was to evaluate the predictive value of plasma D-dimer (D-D) on functional outcome at 90-day follow-up from stroke onset.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational cohort study in the emergency department and enrolled 220 patients with AIS. Plasma D-D concentrations, determined by a particle-enhanced, immunoturbidimetric assay, were measured. Each patient's medical record was reviewed, and demographic, clinical, laboratory and neuroimaging information was abstracted.
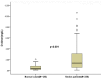
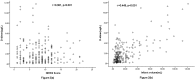
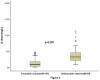
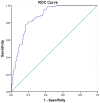
Results: There was a positive correlation between levels of D-D and the NIHSS (r = 0.361, p<0.001), and the infarct volume (r = 0.449, p<0.001). In the 69 patients with an unfavorable functional outcome, D-D levels were higher compared with those in patients with a favorable outcome [3.24(IQR, 2.18-4.60)mg/L vs 0.88(IQR, 0.35-1.77) mg/L; p<0.001]. After adjusting for all other significant outcome predictors, D-D level remained an independent predictor for unfavorable functional outcome and mortality with an odds ratio of 2.18 (95% CI, 1.55-2.83), 3.22 (95% CI, 2.05-6.43); respectively.
Conclusions: D-D levels are a useful tool to predict outcome and mortality 90-day after acute ischemic stroke and have a potential to assist clinicians.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Liu L, Wang D, Wong KSL, Wang Y (2011) Stroke and Stroke Care in China Huge Burden, Significant Workload, and a National Priority. Stroke 42: 3651–3654. - PubMed
-
- Haapaniemi E, Tatlisumak T (2009) Is D-dimer helpful in evaluating stroke patients? A systematic review. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 119: 141–150. - PubMed
-
- Lowe GD, Rumley A (1999) Use of fibrinogen and fibrin D-dimer in prediction of arterial thrombotic events. Thromb Haemost 82: 667–672. - PubMed
-
- Mahé I, Bergmann JF, Chassany O, dit-Sollier CB, Simoneau G, et al. (2012) A multicentric prospective study in usual care: D-dimer and cardiovascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb Res 129: 693–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

