Detecting potential adverse reactions of sulpiride in schizophrenic patients by prescription sequence symmetry analysis
- PMID: 24587038
- PMCID: PMC3937342
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089795
Detecting potential adverse reactions of sulpiride in schizophrenic patients by prescription sequence symmetry analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Previous studies have demonstrated sulpiride to be significantly more effective than haloperidol, risperidone and olanzapine in schizophrenic treatment; however, only limited information is available on the potential risks associated with sulpiride treatment. This study attempts to provide information on the potential risks of sulpiride treatment of schizophrenia, especially with regard to unexpected adverse effects.
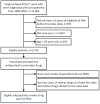
Materials and methods: Patients with schizophrenia aged 18 and older, newly prescribed with a single antipsychotic medication from the National Health Insurance Research Database of Taiwan in the period from 2003 to 2010 were included. A within-subject comparison method, prescription sequence symmetry analysis (PSSA) was employed to efficiently identify potential causal relationships while controlling for potential selection bias.
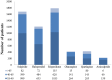
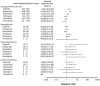
Results: A total of 5,750 patients, with a mean age of 39, approximately half of whom were male, constituted the study cohort. The PSSA found that sulpiride was associated with EPS (adjusted SR, 1.73; 95% CI, 1.46-2.06) and hyperprolactinemia (12.04; 1.59-91.2). In comparison, EPS caused by haloperidol has a magnitude of 1.99 when analyzed with PSSA, and hyperprolactinemia caused by amisulpride has a magnitude of 8.05, respectively. Another finding was the unexpected increase in the use of stomatological corticosteroids, emollient laxatives, dermatological preparations of corticosteroids, quinolone antibacterials, and topical products for joint and muscular pain, after initiation of sulpiride treatment.
Conclusions: We found sulpiride to be associated with an increased risk of EPS and hyperprolactinemia, and the potential risk could be as high as that induced by haloperidol and amisulpride, respectively. Additionally, our study provides grounds for future investigations into the associations between sulpiride and the increased use of additional drugs for managing adverse effects, including stomatological, dermatological, and musculoskeletal or joint side effects, constipation, and pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative risk of oral ulcerations among antipsychotics users - population-based retrospective cohort study.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016 Feb;25(2):123-32. doi: 10.1002/pds.3903. Epub 2015 Nov 9. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016. PMID: 26549190
-
Effectiveness of sulpiride in adult patients with schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2013 May;39(3):673-83. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbs002. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Schizophr Bull. 2013. PMID: 22315480 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic drug use and the risk of seizures: follow-up study with a nested case-control analysis.CNS Drugs. 2015 Jul;29(7):591-603. doi: 10.1007/s40263-015-0262-y. CNS Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26242478
-
Safety profile of amisulpride in short- and long-term use.Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000;400:23-7. doi: 10.1111/j.0065-1591.2000.007s021[dash]5.x. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000. PMID: 10823308 Review.
-
Amisulpride: a review of its use in the management of schizophrenia.CNS Drugs. 2004;18(13):933-56. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200418130-00007. CNS Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15521794 Review.
Cited by
-
Prescribing cascades in community-dwelling adults: A systematic review.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Oct;10(5):e01008. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1008. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 36123967 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Potentially Inappropriate Medications in People With Dementia in Vietnam and Its Associated Factors.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2018 Nov;33(7):423-432. doi: 10.1177/1533317518768999. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2018. PMID: 29642720 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription rate of medications potentially contributing to lower urinary tract symptoms and detection of adverse reactions by prescription sequence symmetry analysis.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2015 Feb 15;1:7. doi: 10.1186/s40780-014-0004-1. eCollection 2015. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2015. PMID: 26819718 Free PMC article.
-
Prescribing Cascades Among Older Community-Dwelling Adults: Application of Prescription Sequence Symmetry Analysis to a National Database in Ireland.Ann Fam Med. 2025 Jul 28;23(4):315-324. doi: 10.1370/afm.240383. Ann Fam Med. 2025. PMID: 40494622 Free PMC article.
-
Selective blockade of spinal D2DR by levo-corydalmine attenuates morphine tolerance via suppressing PI3K/Akt-MAPK signaling in a MOR-dependent manner.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Nov 14;50(11):1-12. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0175-1. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30429454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Zakwani IS, Barron JJ, Bullano MF, Arcona S, Drury CJ, et al. (2003) Analysis of healthcare utilization patterns and adherence in patients receiving typical and atypical antipsychotic medications. Curr Med Res Opin 19: 619–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

