CXCR4 inhibition ameliorates severe obliterative pulmonary hypertension and accumulation of C-kit⁺ cells in rats
- PMID: 24587052
- PMCID: PMC3933653
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089810
CXCR4 inhibition ameliorates severe obliterative pulmonary hypertension and accumulation of C-kit⁺ cells in rats
Abstract
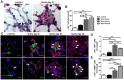
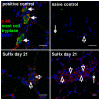
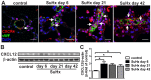
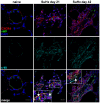
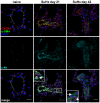
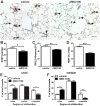
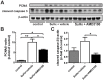
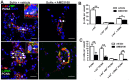
Successful curative treatment of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension with luminal obliteration will require a thorough understanding of the mechanism underlying the development and progression of pulmonary vascular lesions. But the cells that obliterate the pulmonary arterial lumen in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension are incompletely characterized. The goal of our study was to evaluate whether inhibition of CXC chemokine receptor 4 will prevent the accumulation of c-kit⁺ cells and severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. We detected c-kit⁺⁻ cells expressing endothelial (von Willebrand Factor) or smooth muscle cell/myofibroblast (α-smooth muscle actin) markers in pulmonary arterial lesions of SU5416/chronic hypoxia rats. We found increased expression of CXC chemokine ligand 12 in the lung tissue of SU5416/chronic hypoxia rats. In our prevention study, AMD3100, an inhibitor of the CXC chemokine ligand 12 receptor, CXC chemokine receptor 4, only moderately decreased pulmonary arterial obliteration and pulmonary hypertension in SU5416/chronic hypoxia animals. AMD3100 treatment reduced the number of proliferating c-kit⁺ α-smooth muscle actin⁺ cells and pulmonary arterial muscularization and did not affect c-kit⁺ von Willebrand Factor⁺ cell numbers. Both c-kit⁺ cell types expressed CXC chemokine receptor 4. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that in the SU5416/chronic hypoxia model of severe pulmonary hypertension, the CXC chemokine receptor 4-expressing c-kit⁺ α-smooth muscle actin⁺ cells contribute to pulmonary arterial muscularization. In contrast, vascular lumen obliteration by c-kit⁺ von Willebrand Factor⁺ cells is largely independent of CXC chemokine receptor 4.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statin ameliorates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension associated with down-regulated stromal cell-derived factor-1.Cardiovasc Res. 2009 Jan 1;81(1):226-34. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn244. Epub 2008 Sep 8. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 18779230
-
Neutralization of CXCL12 attenuates established pulmonary hypertension in rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Mar 1;116(3):686-697. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz153. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31173066
-
Silibinin efficacy in a rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension using monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia.Respir Res. 2019 Apr 25;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1041-y. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31023308 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of antiangiogenic compound SU5416 in a rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Respiration. 2011;81(3):253-61. doi: 10.1159/000322011. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Respiration. 2011. PMID: 21116108 Review.
-
Progenitor cell mobilization and recruitment: SDF-1, CXCR4, α4-integrin, and c-kit.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;111:243-64. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398459-3.00011-3. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22917234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokines, Chemokines, and Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1303:275-303. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63046-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33788198
-
Sildenafil attenuates hypoxic pulmonary remodelling by inhibiting bone marrow progenitor cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 May;21(5):871-880. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13026. Epub 2016 Nov 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27860185 Free PMC article.
-
Pericytes contribute to pulmonary vascular remodeling via HIF2α signaling.EMBO Rep. 2024 Feb;25(2):616-645. doi: 10.1038/s44319-023-00054-w. Epub 2024 Jan 19. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38243138 Free PMC article.
-
Using extracellular matrix derived from sugen-chronic hypoxia lung tissue to study pulmonary arterial hypertension.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 5;14:1192798. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1192798. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37731734 Free PMC article.
-
HIV X4 Variants Increase Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase in the Pulmonary Microenvironment and are associated with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 16;10(1):11696. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68060-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32678115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simonneau G, Robbins IM, Beghetti M, Channick RN, Delcroix M, et al. (2009) Updated Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 54: S43–S54. - PubMed
-
- Sakao S, Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Lee JD, Wood K, Cool CD, et al. (2005) Initial apoptosis is followed by increased proliferation of apoptosis-resistant endothelial cells. Faseb J 19: 1178–1180. - PubMed
-
- Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Kasahara Y, Alger L, Hirth P, Mc Mahon G, et al. (2001) Inhibition of the VEGF receptor 2 combined with chronic hypoxia causes cell death-dependent pulmonary endothelial cell proliferation and severe pulmonary hypertension. Faseb J 15: 427–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

