Murine model for Fusarium oxysporum invasive fusariosis reveals organ-specific structures for dissemination and long-term persistence
- PMID: 24587124
- PMCID: PMC3937399
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089920
Murine model for Fusarium oxysporum invasive fusariosis reveals organ-specific structures for dissemination and long-term persistence
Abstract
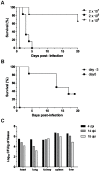
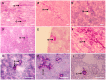
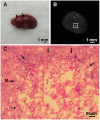
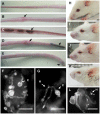
The soil-borne plant pathogen Fusarium oxysporum causes life-threatening invasive fusariosis in immunocompromised individuals. The mechanism of infection in mammalian hosts is largely unknown. In the present study we show that the symptoms of disseminated fusariosis caused by F. oxysporum in immunosuppressed mice are remarkably similar to those reported in humans. Distinct fungal structures were observed inside the host, depending on the infected organ. Invasive hyphae developed in the heart and kidney, causing massive colonization of the organs. By contrast, chlamydospore-like survival structures were found in lung, spleen and liver. Systemically infected mice also developed skin and eye infections, as well as thrombosis and necrosis in the tail. We further show that F. oxysporum can disseminate and persist in the organs of immunocompetent animals, and that these latent infections can lead to lethal systemic fusariosis if the host is later subjected to immunosuppressive treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of intratracheal Fusarium solani inoculation in immunocompetent mice.Microb Pathog. 2019 Mar;128:317-322. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.01.020. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30660735
-
Fosmanogepix (APX001) Is Effective in the Treatment of Immunocompromised Mice Infected with Invasive Pulmonary Scedosporiosis or Disseminated Fusariosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Feb 21;64(3):e01735-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01735-19. Print 2020 Feb 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31818813 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive fusariosis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023 Dec 20;36(4):e0015922. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00159-22. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37937988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emergence of zoonotic Fusarium oxysporum infection in captive-reared fingerlings of golden mahseer, Tor putitora (Hamilton, 1822) from the central Himalayan region of India.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020 Mar;67(2):555-563. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13367. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020. PMID: 31539213
-
Fusariosis, a complex infection caused by a high diversity of fungal species refractory to treatment.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Dec;32(12):1491-500. doi: 10.1007/s10096-013-1924-7. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23934595 Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal model systems and the elucidation of pathogenicity determinants.Fungal Genet Biol. 2014 Sep;70(100):42-67. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Fungal Genet Biol. 2014. PMID: 25011008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dual Pathogen Fusarium: Diseases, Incidence, Azole Resistance, and Biofilms.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Apr 9;11(4):294. doi: 10.3390/jof11040294. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial hitchhikers derive benefits from fungal housing.Curr Biol. 2022 Apr 11;32(7):1523-1533.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.017. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35235767 Free PMC article.
-
Multiresistant Fusarium Pathogens on Plants and Humans: Solutions in (from) the Antifungal Pipeline?Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Nov 28;12:3727-3737. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S180912. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31819555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Janus-Faced Molecules against Plant Pathogenic Fungi.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 15;22(22):12323. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212323. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Naggie S, Perfect JR (2009) Molds: hyalohyphomycosis, phaeohyphomycosis, and zygomycosis. Clin Chest Med 30: 337–353, vii–viii. - PubMed
-
- Dignani MC, Anaissie E (2004) Human fusariosis. Clin Microbiol Infect 10 Suppl 167–75. - PubMed
-
- Rotowa NA, Shadomy HJ, Shadomy S (1990) In vitro activities of polyene and imidazole antifungal agents against unusual opportunistic fungal pathogens. Mycoses 33: 203–211. - PubMed
-
- Anaissie E, Paetznick V, Proffitt R, Adler-Moore J, Bodey GP (1991) Comparison of the in vitro antifungal activity of free and liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 10: 665–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

