Electroacupuncture promotes post-stroke functional recovery via enhancing endogenous neurogenesis in mouse focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 24587178
- PMCID: PMC3933702
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090000
Electroacupuncture promotes post-stroke functional recovery via enhancing endogenous neurogenesis in mouse focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
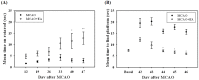
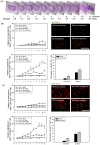
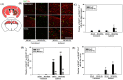
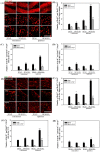
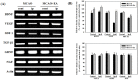
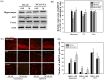
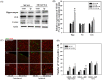
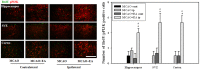
To investigate the question of whether electroacupuncture (EA) promotes functional recovery via enhancement of proliferation and differentiation of neuronal stem cells (NSCs) in ischemic stroke, EA stimulation with 2 Hz was applied at bilateral acupoints to Baihui (GV20) and Dazhui (GV14) in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice. EA stimulation improved neuromotor function and cognitive ability after ischemic stroke. EA stimulation resulted in an increase in the number of proliferated cells, especially in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the ipsilateral hemisphere. Although a very limited number of NSCs survived and differentiated into neurons or astrocytes, EA treatment resulted in a significant increase in the number of proliferative cells and differentiated cells in the hippocampus and SVZ of the ipsilateral hemisphere compared to MCAO mice. EA stimulation resulted in significantly increased mRNA expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Protein levels of these factors were confirmed in the ipsilateral hippocampus and SVZ by immunohistochemical and Western blotting analyses. Expression of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, BDNF, and VEGF-mediated down-stream were enhanced by EA stimulation in newly formed neuroblasts. These results indicate that EA treatment after ischemic stroke may promote post-stroke functional recovery by enhancement of proliferation and differentiation of NSCs via the BDNF and VEGF signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subacute electroacupuncture at Baihui (GV 20) and Dazhui (GV 14) promotes post-stroke functional recovery via neurogenesis and astrogliosis in a photothrombotic stroke mouse model.J Tradit Chin Med. 2019 Dec;39(6):833-841. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 32186154
-
Potential benefits of mesenchymal stem cells and electroacupuncture on the trophic factors associated with neurogenesis in mice with ischemic stroke.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 1;8(1):2044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20481-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29391466 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of a Combination of Electroacupuncture and TrkB-Expressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;56(1):157-173. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1067-z. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29682700
-
Effect of Wnt signaling pathway on neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia and its therapeutic potential.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Nov;164:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32763283 Review.
-
Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Oct;44(5):859-870. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240828.008. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39380217 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The factors affecting neurogenesis after stroke and the role of acupuncture.Front Neurol. 2023 Jan 20;14:1082625. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1082625. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36741282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture enhances rehabilitation through miR-181b targeting PirB after ischemic stroke.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 14;6:38997. doi: 10.1038/srep38997. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27966582 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 2-Week Naringin Supplementation on Neurogenesis and BDNF Levels in Ischemia-Reperfusion Model of Rats.Neuromolecular Med. 2024 Mar 8;26(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s12017-023-08771-0. Neuromolecular Med. 2024. PMID: 38457013 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture for the treatment of ischemic stroke: A preclinical meta-analysis and systematic review.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Mar 1;21(3):1191-1210. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01030. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 39885673 Free PMC article.
-
Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation Promotes Motor Functional Recovery by Enhancing Oligodendrocyte Survival and Differentiation and by Protecting Myelin after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Neurosci Bull. 2020 Apr;36(4):372-384. doi: 10.1007/s12264-019-00442-0. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Neurosci Bull. 2020. PMID: 31732865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287: 1433–1438. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenwalner RJ, Parent JM (2006) Adult neurogenesis and the ischemic forebrain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26: 1–20. - PubMed
-
- Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M (2005) Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev 85: 523–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

