Elevated exhaled nitric oxide in allergen-provoked asthma is associated with airway epithelial iNOS
- PMID: 24587191
- PMCID: PMC3938593
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090018
Elevated exhaled nitric oxide in allergen-provoked asthma is associated with airway epithelial iNOS
Abstract
Background: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide is elevated in allergen-provoked asthma. The cellular and molecular source of the elevated fractional exhaled nitric oxide is, however, uncertain.
Objective: To investigate whether fractional exhaled nitric oxide is associated with increased airway epithelial inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in allergen-provoked asthma.
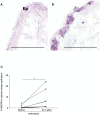
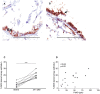
Methods: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide was measured in healthy controls (n = 14) and allergic asthmatics (n = 12), before and after bronchial provocation to birch pollen out of season. Bronchoscopy was performed before and 24 hours after allergen provocation. Bronchial biopsies and brush biopsies were processed for nitric oxide synthase activity staining with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase (NADPH-d), iNOS immunostaining, or gene expression analysis of iNOS by real-time PCR. NADPH-d and iNOS staining were quantified using automated morphometric analysis.
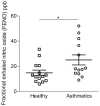
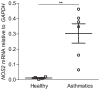
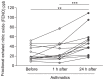
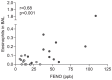
Results: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide and expression of iNOS mRNA were significantly higher in un-provoked asthmatics, compared to healthy controls. Allergic asthmatics exhibited a significant elevation of fractional exhaled nitric oxide after allergen provocation, as well as an accumulation of airway eosinophils. Moreover, nitric oxide synthase activity and expression of iNOS was significantly increased in the bronchial epithelium of asthmatics following allergen provocation. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide correlated with eosinophils and iNOS expression.
Conclusion: Higher fractional exhaled nitric oxide concentration among asthmatics is associated with elevated iNOS mRNA in the bronchial epithelium. Furthermore, our data demonstrates for the first time increased expression and activity of iNOS in the bronchial epithelium after allergen provocation, and thus provide a mechanistic explanation for elevated fractional exhaled nitric oxide in allergen-provoked asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurement with conventional tests in steroid-naive asthma patients.J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2006;16(4):239-46. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16889281
-
Comparison of inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA expression in different airway portions and association with nitric oxide parameters from patients with asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2019 May;49(5):582-590. doi: 10.1111/cea.13344. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019. PMID: 30667100 Free PMC article.
-
IL-13 induced increases in nitrite levels are primarily driven by increases in inducible nitric oxide synthase as compared with effects on arginases in human primary bronchial epithelial cells.Clin Exp Allergy. 2008 Jun;38(6):936-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.02969.x. Epub 2008 Apr 1. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008. PMID: 18384429 Free PMC article.
-
[Nitric oxide in bronchial asthma].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002 Jun;12(72):519-21. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002. PMID: 12362674 Review. Polish.
-
Understanding the Cellular Sources of the Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) and Its Role as a Biomarker of Type 2 Inflammation in Asthma.Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 2;2022:5753524. doi: 10.1155/2022/5753524. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35547356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide System and Bronchial Epithelium: More Than a Barrier.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 30;12:687381. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.687381. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34276407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Oscillometry in Pediatric Asthma.Respir Care. 2025 Jun;70(6):632-639. doi: 10.1089/respcare.12674. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Respir Care. 2025. PMID: 40028857 Review.
-
A review of epigenetic changes in asthma: methylation and acetylation.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Mar 29;13(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01049-x. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33781317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between FeNO, Total Blood IgE, Peripheral Blood Eosinophil and Inflammatory Cytokines in Partly Controlled Asthma.J Asthma Allergy. 2020 Oct 29;13:533-543. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S274022. eCollection 2020. J Asthma Allergy. 2020. PMID: 33149625 Free PMC article.
-
Bioenergetic Differences in the Airway Epithelium of Lean Versus Obese Asthmatics Are Driven by Nitric Oxide and Reflected in Circulating Platelets.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Oct 1;31(10):673-686. doi: 10.1089/ars.2018.7627. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 30608004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (2007) Global surveillance,prevention and control of chronic respiratory diseases: a comprehensive approach. In: Organization WH, editor. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization.
-
- Kharitonov S, Yates D, Robbins R, Logan-Sinclair R, Shinebourne E, et al. (1994) Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet 343: 133–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

