Modulation of basophils' degranulation and allergy-related enzymes by monomeric and dimeric naphthoquinones
- PMID: 24587235
- PMCID: PMC3938571
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090122
Modulation of basophils' degranulation and allergy-related enzymes by monomeric and dimeric naphthoquinones
Abstract
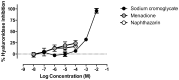
Allergic disorders are characterized by an abnormal immune response towards non-infectious substances, being associated with life quality reduction and potential life-threatening reactions. The increasing prevalence of allergic disorders demands for new and effective anti-allergic treatments. Here we test the anti-allergic potential of monomeric (juglone, menadione, naphthazarin, plumbagin) and dimeric (diospyrin and diosquinone) naphthoquinones. Inhibition of RBL-2H3 rat basophils' degranulation by naphthoquinones was assessed using two complementary stimuli: IgE/antigen and calcium ionophore A23187. Additionally, we tested for the inhibition of leukotrienes production in IgE/antigen-stimulated cells, and studied hyaluronidase and lipoxidase inhibition by naphthoquinones in cell-free assays. Naphthazarin (0.1 µM) decreased degranulation induced by IgE/antigen but not A23187, suggesting a mechanism upstream of the calcium increase, unlike diospyrin (10 µM) that reduced degranulation in A23187-stimulated cells. Naphthoquinones were weak hyaluronidase inhibitors, but all inhibited soybean lipoxidase with the most lipophilic diospyrin, diosquinone and menadione being the most potent, thus suggesting a mechanism of competition with natural lipophilic substrates. Menadione was the only naphthoquinone reducing leukotriene C4 production, with a maximal effect at 5 µM. This work expands the current knowledge on the biological properties of naphthoquinones, highlighting naphthazarin, diospyrin and menadione as potential lead compounds for structural modification in the process of improving and developing novel anti-allergic drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH (2006) The regulation of allergy and asthma. Immunol Rev 212: 238–255. - PubMed
-
- Holgate ST (1999) The epidemic of allergy and asthma. Nature 402: B2–4. - PubMed
-
- Anand P, Singh B, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2012) Mast cells: an expanding pathophysiological role from allergy to other disorders. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 385: 657–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

