Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus among adults at high risk for HIV transmission two decades after implementation of nationwide hepatitis B virus vaccination program in Taiwan
- PMID: 24587275
- PMCID: PMC3935970
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090194
Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus among adults at high risk for HIV transmission two decades after implementation of nationwide hepatitis B virus vaccination program in Taiwan
Abstract
Background: Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) after implementation of universal neonatal HBV vaccination and catch-up vaccination programs remains rarely investigated among the adults who were born in the vaccination era (in or after 1986) and engaged in high-risk sexual behaviors.
Materials and methods: Between 2006 and 2012, we determined HBV surface antigen ([HBsAg), anti-HBs, and HBV core antibody (anti-HBc), hepatitis C virus antibody (anti-HCV) and rapid plasma reagin titers among HIV-infected men who have sex with men (MSM) born during 1984-1985 (Group I: 244 persons) and those born in or after 1986 (Group II: 523), and HIV-uninfected MSM (Group III: 377) and heterosexuals (Group IV: 217) born in or after 1986. Prevalence and incidence of HBV infection were estimated and multivariate analysis was performed to identify factors associated with HBsAg positivity.
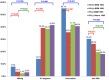
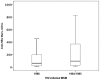
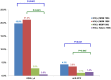
Results: Compared with Group I, Groups II-IV had a significantly lower prevalence of HBsAg positivity (7.8% vs 3.7%, 2.4%, and 3.2%, respectively); and the prevalence of anti-HBc positivity was also lower for Groups III and IV (30.3% vs. 19.6%, and 18.0%, respectively), but no difference was observed between Groups I and II (30.3% vs. 26.3%). In multivariate analysis, HBsAg positivity was significantly associated with syphilis (adjusted odds ratio, 2.990; 95% confidence interval, 1.502-5.953) and anti-HCV positivity (adjusted odds ratio, 3.402; 95% confidence interval, 1.091-10.614). In subjects of Group II with all-negative HBV markers at baseline, the incidence rate of HBsAg seroconversion was 0.486 episodes per 100 person-years; and for those who received combination antiretroviral therapy containing lamivudine and/or tenofovir, none developed HBsAg seroconversion during the follow-up.
Conclusions: Among the adults who were born in or after 1986 and engaged in high-risk sexual behaviors in Taiwan, neonatal HBV vaccination and catch-up vaccination programs conferred long-term protection against HBsAg seroconversion and HBsAg positivity was associated with syphilis and anti-HCV positivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus seroprevalence among HIV-infected patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy three decades after universal neonatal hepatitis B immunization program in Taiwan.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021 Apr;54(2):228-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2019.10.005. Epub 2019 Oct 30. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021. PMID: 31708481
-
Seroprevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection among taiwanese human immunodeficiency virus type 1-positive persons in the era of nationwide hepatitis B vaccination.Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Apr;104(4):877-84. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2008.159. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19259078
-
Seroprevalence of hepatitis virus infection in men who have sex with men aged 18-40 years in Taiwan.J Formos Med Assoc. 2012 Aug;111(8):431-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2011.06.022. Epub 2012 Mar 8. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012. PMID: 22939661
-
Hepatitis B virus seroepidemiology data for Africa: Modelling intervention strategies based on a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2020 Apr 21;17(4):e1003068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003068. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32315297 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Cure of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Individuals With HIV-Coinfection: A Literature Review.Viruses. 2021 Jul 11;13(7):1341. doi: 10.3390/v13071341. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
International Congress of Drug Therapy in HIV Infection 23-26 October 2016, Glasgow, UK.J Int AIDS Soc. 2016 Oct 23;19(8(Suppl 7)):21487. doi: 10.7448/IAS.19.8.21487. eCollection 2016. J Int AIDS Soc. 2016. PMID: 27780519 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multicenter study of skin rashes and hepatotoxicity in antiretroviral-naïve HIV-positive patients receiving non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor plus nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors in Taiwan.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 21;12(2):e0171596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171596. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28222098 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence and associated factors of hepatitis B virus infection among HIV-positive adults attending an antiretroviral treatment clinic at Wolaita Sodo University Referral Hospital.Hepat Med. 2019 Sep 6;11:137-147. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S206870. eCollection 2019. Hepat Med. 2019. PMID: 31565003 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus coinfection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a review.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 28;20(40):14598-614. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14598. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25356024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of hepatitis B and C infections among HIV-positive men who have sex with men: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 26;7(6):e2206. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.2206. eCollection 2024 Jun. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38933421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease C, Prevention (2006) Hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults – United States, 2004. MMWR Morbidity and mortality weekly report 55: 509–511. - PubMed
-
- Su WJ, Liu CC, Liu DP, Chen SF, Huang JJ, et al. (2012) Effect of age on the incidence of acute hepatitis B after 25 years of a universal newborn hepatitis B immunization program in Taiwan. The Journal of infectious diseases 205: 757–762. - PubMed
-
- McMahon BJ, Bulkow LR, Singleton RJ, Williams J, Snowball M, et al. (2011) Elimination of hepatocellular carcinoma and acute hepatitis B in children 25 years after a hepatitis B newborn and catch-up immunization program. Hepatology 54: 801–807. - PubMed
-
- Chen SM, Kung CM, Yang WJ, Wang HL (2011) Efficacy of the nationwide hepatitis B infant vaccination program in Taiwan. Journal of clinical virology: the official publication of the Pan American Society for Clinical Virology 52: 11–16. - PubMed
-
- Chang MH, Chen CJ, Lai MS, Hsu HM, Wu TC, et al. (1997) Universal hepatitis B vaccination in Taiwan and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in children. Taiwan Childhood Hepatoma Study Group. The New England journal of medicine 336: 1855–1859. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

