Characterisation of connexin expression and electrophysiological properties in stable clones of the HL-1 myocyte cell line
- PMID: 24587307
- PMCID: PMC3938655
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090266
Characterisation of connexin expression and electrophysiological properties in stable clones of the HL-1 myocyte cell line
Abstract
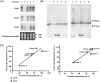
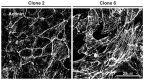
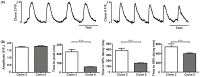
The HL-1 atrial line contains cells blocked at various developmental stages. To obtain homogeneous sub-clones and correlate changes in gene expression with functional alterations, individual clones were obtained and characterised for parameters involved in conduction and excitation-contraction coupling. Northern blots for mRNAs coding for connexins 40, 43 and 45 and calcium handling proteins (sodium/calcium exchanger, L- and T-type calcium channels, ryanodine receptor 2 and sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2) were performed. Connexin expression was further characterised by western blots and immunofluorescence. Inward currents were characterised by voltage clamp and conduction velocities measured using microelectrode arrays. The HL-1 clones had similar sodium and calcium inward currents with the exception of clone 2 which had a significantly smaller calcium current density. All the clones displayed homogenous propagation of electrical activity across the monolayer correlating with the levels of connexin expression. Conduction velocities were also more sensitive to inhibition of junctional coupling by carbenoxolone (∼ 80%) compared to inhibition of the sodium current by lidocaine (∼ 20%). Electrical coupling by gap junctions was the major determinant of conduction velocities in HL-1 cell lines. In summary we have isolated homogenous and stable HL-1 clones that display characteristics distinct from the heterogeneous properties of the original cell line.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A novel mechanism of tandem activation of ryanodine receptors by cytosolic and SR luminal Ca2+ during excitation-contraction coupling in atrial myocytes.J Physiol. 2017 Jun 15;595(12):3835-3845. doi: 10.1113/JP273611. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28028837 Free PMC article.
-
Altered action potential dynamics in electrically remodeled canine atria: evidence for altered intracellular Ca2+ handling.Circ J. 2006 Nov;70(11):1488-96. doi: 10.1253/circj.70.1488. Circ J. 2006. PMID: 17062976
-
Cardiac G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 ablation induces a novel Ca2+ handling phenotype resistant to adverse alterations and remodeling after myocardial infarction.Circulation. 2012 May 1;125(17):2108-18. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.044255. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22496128 Free PMC article.
-
T-tubule remodelling and ryanodine receptor organization modulate sodium-calcium exchange.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:375-83. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_32. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224896 Review.
-
Old cogs, new tricks: a scaffolding role for connexin43 and a junctional role for sodium channels?FEBS Lett. 2014 Apr 17;588(8):1244-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.01.026. Epub 2014 Jan 28. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24486012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coagulation Factor Xa Has No Effects on the Expression of PAR1, PAR2, and PAR4 and No Proinflammatory Effects on HL-1 Cells.Cells. 2023 Dec 15;12(24):2849. doi: 10.3390/cells12242849. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132169 Free PMC article.
-
Rotor Tracking Using Phase of Electrograms Recorded During Atrial Fibrillation.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017 Apr;45(4):910-923. doi: 10.1007/s10439-016-1766-4. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 27921187 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental models of cardiac physiology and pathology.Heart Fail Rev. 2019 Jul;24(4):601-615. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09769-2. Heart Fail Rev. 2019. PMID: 30666533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology of the cardiac myocyte in heart disease.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jul 15;27(14):2149-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-01-0038. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27418636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic recovery of impulse propagation in myocardial infarction via silicon carbide semiconductive nanowires.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 10;13(1):6. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27637-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35013167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhavan A, Atanasiu R, Shrier A (2003) Identification of a COOH-terminal segment involved in maturation and stability of human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channels. J Biol Chem 278: 40105–40112. - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp P, Yamada KA, Baertschi AJ, Green K, Kanter EM, et al. (2006) Relative contributions of connexins 40 and 43 to atrial impulse propagation in synthetic strands of neonatal and fetal murine cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 99: 1216–1224. - PubMed
-
- Coppen SR, Dupont E, Rothery S, Severs NJ (1998) Connexin45 expression is preferentially associated with the ventricular conduction system in mouse and rat heart. Circ Res 82: 232–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

