Assessing the impact of deforestation of the Atlantic rainforest on ant-fruit interactions: a field experiment using synthetic fruits
- PMID: 24587341
- PMCID: PMC3936012
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090369
Assessing the impact of deforestation of the Atlantic rainforest on ant-fruit interactions: a field experiment using synthetic fruits
Abstract
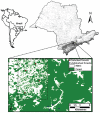
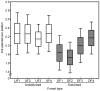
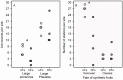
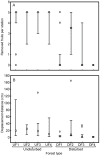
Ants frequently interact with fleshy fruits on the ground of tropical forests. This interaction is regarded as mutualistic because seeds benefit from enhanced germination and dispersal to nutrient-rich microsites, whereas ants benefit from consuming the nutritious pulp/aril. Considering that the process of deforestation affects many attributes of the ecosystem such as species abundance and composition, and interspecific interactions, we asked whether the interaction between ants and fallen fleshy fruits in the Brazilian Atlantic forest differs between human-created fragments and undisturbed forests. We controlled diaspore type and quantity by using synthetic fruits (a plastic 'seed' covered by a lipid-rich 'pulp'), which were comparable to lipid-rich fruits. Eight independent areas (four undisturbed forests, and four disturbed forest fragments) were used in the field experiment, in which we recorded the attracted ant species, ant behaviour, and fruit removal distance. Fruits in undisturbed forest sites attracted a higher number of species than those in disturbed forests. Moreover, the occurrence of large, fruit-carrying ponerine ants (Pachycondyla, Odontomachus; 1.1 to 1.4 cm) was higher in undisturbed forests. Large species (≥3 mm) of Pheidole (Myrmicinae), also able to remove fruits, did not differ between forest types. Following these changes in species occurrence, fruit displacement was more frequent in undisturbed than in disturbed forests. Moreover, displacement distances were also greater in the undisturbed forests. Our data suggest that fallen fleshy fruits interacting with ants face different fates depending on the conservation status of the forest. Together with the severe loss of their primary dispersers in human-disturbed tropical forest sites, vertebrate-dispersed fruits may also be deprived of potential ant-derived benefits in these habitats due to shifts in the composition of interacting ant species. Our data illustrate the use of synthetic fruits to better understand the ecology of ant-fruit interactions in variable ecological settings, including human-disturbed landscapes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Fahrig L (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics 34: 487–515.
-
- Laurance WF, Camargo JLC, Luizão RCC, Laurance SG, Pimm SL, et al. (2011) The fate of Amazonian forest fragments: A 32-year investigation. Biological Conservation 144: 56–67.
-
- Aizen MA, Feinsinger P (1994) Habitat fragmentation, native insect pollinators, and feral honey bees in Argentine ‘Chaco Serrano’. Ecological Applications 4: 378–392.
-
- Tylianakis JM, Tscharntke T, Lewis OT (2007) Habitat modification alters the structure of tropical host-parasitoid food webs. Nature 445: 202–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

