Bacterial antagonists of fungal pathogens also control root-knot nematodes by induced systemic resistance of tomato plants
- PMID: 24587352
- PMCID: PMC3938715
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090402
Bacterial antagonists of fungal pathogens also control root-knot nematodes by induced systemic resistance of tomato plants
Abstract
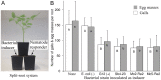
The potential of bacterial antagonists of fungal pathogens to control the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita was investigated under greenhouse conditions. Treatment of tomato seeds with several strains significantly reduced the numbers of galls and egg masses compared with the untreated control. Best performed Bacillus subtilis isolates Sb4-23, Mc5-Re2, and Mc2-Re2, which were further studied for their mode of action with regard to direct effects by bacterial metabolites or repellents, and plant mediated effects. Drenching of soil with culture supernatants significantly reduced the number of egg masses produced by M. incognita on tomato by up to 62% compared to the control without culture supernatant. Repellence of juveniles by the antagonists was shown in a linked twin-pot set-up, where a majority of juveniles penetrated roots on the side without inoculated antagonists. All tested biocontrol strains induced systemic resistance against M. incognita in tomato, as revealed in a split-root system where the bacteria and the nematodes were inoculated at spatially separated roots of the same plant. This reduced the production of egg masses by up to 51%, while inoculation of bacteria and nematodes in the same pot had only a minor additive effect on suppression of M. incognita compared to induced systemic resistance alone. Therefore, the plant mediated effect was the major reason for antagonism rather than direct mechanisms. In conclusion, the bacteria known for their antagonistic potential against fungal pathogens also suppressed M. incognita. Such "multi-purpose" bacteria might provide new options for control strategies, especially with respect to nematode-fungus disease complexes that cause synergistic yield losses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Trudgill DL, Blok VC (2001) Apomictic, polyphagous root-knot nematodes: exceptionally successful and damaging biotrophic root pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39: 53–77. - PubMed
-
- Sasser JN, Eisenback JD, Carter CC, Triantaphyllou AC (1983) The international Meloidogyne project - its goals and accomplishments. Annu Rev Phytopathol 21: 271–288.
-
- Atkinson GF (1892) Some diseases of cotton. Ala Agric Exp St Bull 41: 65 pp.
-
- Hussey RS, McGuire JM (1987) Interactions with other organisms. In: Brown RH, Kerry BR, editors. Principles and Practice of Nematode Control in Crops. Marrickville, Australia: Academic Press. pp. 294–320.
-
- Back MA, Haydock PPJ, Jenkinson P (2002) Disease complexes involving plant parasitic nematodes and soilborne pathogens. Plant Pathology 51: 683–697.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

