Autoreactive IgE is prevalent in systemic lupus erythematosus and is associated with increased disease activity and nephritis
- PMID: 24587356
- PMCID: PMC3938730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090424
Autoreactive IgE is prevalent in systemic lupus erythematosus and is associated with increased disease activity and nephritis
Abstract
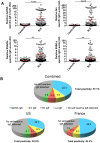
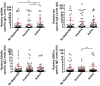
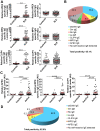
The presence of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus, particularly those of the IgG subclass, have long been associated with disease onset and activity. Here we explored the prevalence of autoreactive IgE in SLE and its relevance to disease in French (n = 79) and United States (US) (n = 117) cohorts with a mean age of 41.5 ± 12.7 and 43.6 ± 15.3 years and disease duration of 13.5 ± 8.5 and 16.6 ± 11.9 years, respectively. Our findings show that approximately 65% of all SLE subjects studied produced IgE antibodies to the seven autoantigens tested. This positivity was increased to almost 83% when only those subjects with active disease were considered. SLE subjects who were positive for anti-dsDNA, -Sm, and -SSB/La -specific IgE showed a highly significant association in the levels of these antibodies with disease activity similar to that of the corresponding IgG's. A strong association of IgE autoantibodies with active nephritis was also found in the combined cohort analysis. A test of the predictive value of autoreactive IgE's and IgGs for disease activity (SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) ≥ 4) revealed that the best predictors were dsDNA-specific IgE and IgG, and that the age of an SLE subject influenced this predictive model. The finding argue that the overall levels of IgE autoantibodies, independently or in combination with IgG autoantibodies, may serve as indicators of active disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Frieri M (2013) Mechanisms of disease for the clinician: systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 110: 228–232. - PubMed
-
- Sawalha AH, Harley JB (2004) Antinuclear autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 16: 534–540. - PubMed
-
- Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, et al. (2003) Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349: 1526–1533. - PubMed
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA (2008) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 358: 929–939. - PubMed
-
- Schroeder K, Herrmann M, Winkler TH (2012) The role of somatic hypermutation in the generation of pathogenic antibodies in SLE. Autoimmunity 46: 121–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

