Sulforaphane inhibits invasion via activating ERK1/2 signaling in human glioblastoma U87MG and U373MG cells
- PMID: 24587385
- PMCID: PMC3938755
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090520
Sulforaphane inhibits invasion via activating ERK1/2 signaling in human glioblastoma U87MG and U373MG cells
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma has highly invasive potential, which might result in poor prognosis and therapeutic failure. Hence, the key we study is to find effective therapies to repress migration and invasion. Sulforaphane (SFN) was demonstrated to inhibit cell growth in a variety of tumors. Here, we will further investigate whether SFN inhibits migration and invasion and find the possible mechanisms in human glioblastoma U87MG and U373MG cells.
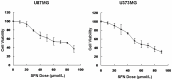
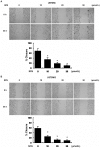
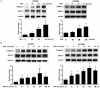
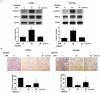
Methods: First, the optimal time and dose of SFN for migration and invasion study were determined via cell viability and cell morphological assay. Further, scratch assay and transwell invasion assay were employed to investigate the effect of SFN on migration and invasion. Meanwhile, Western blots were used to detect the molecular linkage among invasion related proteins phosphorylated ERK1/2, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and CD44v6. Furthermore, Gelatin zymography was performed to detect the inhibition of MMP-2 activation. In addition, ERK1/2 blocker PD98059 (25 µM) was integrated to find the link between activated ERK1/2 and invasion, MMP-2 and CD44v6.
Results: The results showed that SFN (20 µM) remarkably reduced the formation of cell pseudopodia, indicating that SFN might inhibit cell motility. As expected, scratch assay and transwell invasion assay showed that SFN inhibited glioblastoma cell migration and invasion. Western blot and Gelatin zymography showed that SFN phosphorylated ERK1/2 in a sustained way, which contributed to the downregulated MMP-2 expression and activity, and the upregulated CD44v6 expression. These molecular interactions resulted in the inhibition of cell invasion.
Conclusions: SFN inhibited migration and invasion processes. Furthermore, SFN inhibited invasion via activating ERK1/2 in a sustained way. The accumulated ERK1/2 activation downregulated MMP-2 expression and decreased its activity and upregulated CD44v6. SFN might be a potential therapeutic agent by activating ERK1/2 signaling against human glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sulforaphane inhibits invasion by phosphorylating ERK1/2 to regulate E-cadherin and CD44v6 in human prostate cancer DU145 cells.Oncol Rep. 2015 Sep;34(3):1565-72. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4098. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26134113
-
Sulforaphane-cysteine induces apoptosis by sustained activation of ERK1/2 and caspase 3 in human glioblastoma U373MG and U87MG cells.Oncol Rep. 2017 May;37(5):2829-2838. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5562. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28393231
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin β induces cell motility via ERK1/2 and MMP-2 activation in human glioblastoma U87MG cells.J Neurooncol. 2013 Feb;111(3):237-44. doi: 10.1007/s11060-012-1017-y. Epub 2012 Dec 13. J Neurooncol. 2013. PMID: 23232806
-
Progress in the development of ERK1/2 inhibitors for treating cancer and other diseases.Adv Pharmacol. 2024;100:181-207. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2024.04.001. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Adv Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39034052 Review.
-
Sulforaphane's Role in Osteosarcoma Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 25;13(5):1048. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051048. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426874 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sulforaphane Causes Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Glioblastoma U87MG and U373MG Cell Lines under Hypoxic Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 18;22(20):11201. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011201. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681862 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in natural dietary non-phenolic bioactives on cancers metastasis.J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Jul;26(3):940-964. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Food Drug Anal. 2018. PMID: 29976413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulforaphane suppresses oral cancer cell migration by regulating cathepsin S expression.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 3;9(25):17564-17575. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24786. eCollection 2018 Apr 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29707130 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder Cancer Metastasis Induced by Chronic Everolimus Application Can Be Counteracted by Sulforaphane In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 4;21(15):5582. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155582. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32759798 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Efficacy and Involvement of AKT, mTOR, and ERK Kinases in the Mechanism of Sulforaphane against Endometrial Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 18;12(5):1273. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051273. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32443471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart LA (2002) Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet 359: 1011–1018. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Roila F (2009) Malignant glioma: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 20 Suppl 4126–128. - PubMed
-
- Gielen PR, Aftab Q, Ma N, Chen VC, Hong X, et al. (2013) Connexin43 confers Temozolomide resistance in human glioma cells by modulating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Neuropharmacology 75: 539–48. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain MC (2010) Temozolomide: therapeutic limitations in the treatment of adult high-grade gliomas. Expert Rev Neurother 10: 1537–1544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

