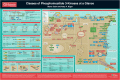
Classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases at a glance
- PMID: 24587488
- PMCID: PMC3937771
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.093773
Classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases at a glance
Abstract
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) family is important to nearly all aspects of cell and tissue biology and central to human cancer, diabetes and aging. PI3Ks are spatially regulated and multifunctional, and together, act at nearly all membranes in the cell to regulate a wide range of signaling, membrane trafficking and metabolic processes. There is a broadening recognition of the importance of distinct roles for each of the three different PI3K classes (I, II and III), as well as for the different isoforms within each class. Ongoing issues include the need for a better understanding of the in vivo complexity of PI3K regulation and cellular functions. This Cell Science at a Glance article and the accompanying poster summarize the biochemical activities, cellular roles and functional requirements for the three classes of PI3Ks. In doing so, we aim to provide an overview of the parallels, the key differences and crucial interplays between the regulation and roles of the three PI3K classes.
Keywords: Class I PI3K; Class II PI3K; Class III PI3K; PI3-kinases; PI3K; Phosphoinositide.
References
-
- Biswas K., Yoshioka K., Asanuma K., Okamoto Y., Takuwa N., Sasaki T., Takuwa Y. (2013). Essential role of class II phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-C2α in sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1-mediated signaling and migration in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 2325–2339 10.1074/jbc.M112.409656 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources